方法安全性
除了在请求级别对授权进行建模外, Spring Security 还支持在方法级别进行建模。
您可以通过使用任何 XML 配置文件注释任何类或将其添加到任何 XML 配置文件来在应用程序中激活它,如下所示:@Configuration@EnableMethodSecurity<method-security>
-
Java
-
Kotlin
-
Xml
@EnableMethodSecurity@EnableMethodSecurity<sec:method-security/>然后,您可以立即使用 @PreAuthorize、@PostAuthorize、@PreFilter 和 @PostFilter 注释任何 Spring 管理的类或方法,以授权方法调用,包括输入参数和返回值。
| 默认情况下,Spring Boot Starter Security 不激活方法级授权。 |
Method Security 还支持许多其他用例,包括 AspectJ 支持、自定义注释和几个配置点。 考虑了解以下使用案例:
-
了解方法安全性的工作原理以及使用它的原因
-
使用
@PreAuthorize和@PostAuthorize授权方法 -
使用
@PreFilter和@PostFilter的筛选方法 -
使用 JSR-250 注解授权方法
-
使用 AspectJ 表达式授权方法
-
与 AspectJ 字节码编织集成
-
自定义 SpEL 表达式处理
方法安全性的工作原理
Spring Security 的方法授权支持对于以下方面非常方便:
-
提取细粒度的授权逻辑;例如,当 method parameters 和 return values 对授权决策有贡献时。
-
在服务层实施安全性
-
在风格上更倾向于基于 Comments 的配置,而不是基于 的配置
HttpSecurity
由于 Method Security 是使用 Spring AOP 构建的,因此您可以访问其所有表达能力,以根据需要覆盖 Spring Security 的默认值。
如前所述,您首先要添加到类或 Spring XML 配置文件中。@EnableMethodSecurity@Configuration<sec:method-security/>
|
此注释和 XML 元素分别取代 和 。
它们提供了以下改进:
如果您使用的是 或 ,则这些选项现已弃用,建议您迁移。 |
方法授权是方法授权之前和方法之后授权的组合。 考虑以下列方式注释的服务 Bean:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Service
public class MyCustomerService {
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('permission:read')")
@PostAuthorize("returnObject.owner == authentication.name")
public Customer readCustomer(String id) { ... }
}@Service
open class MyCustomerService {
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('permission:read')")
@PostAuthorize("returnObject.owner == authentication.name")
fun readCustomer(val id: String): Customer { ... }
}激活 Method Security 时,给定的 invokeation to 可能如下所示:MyCustomerService#readCustomer
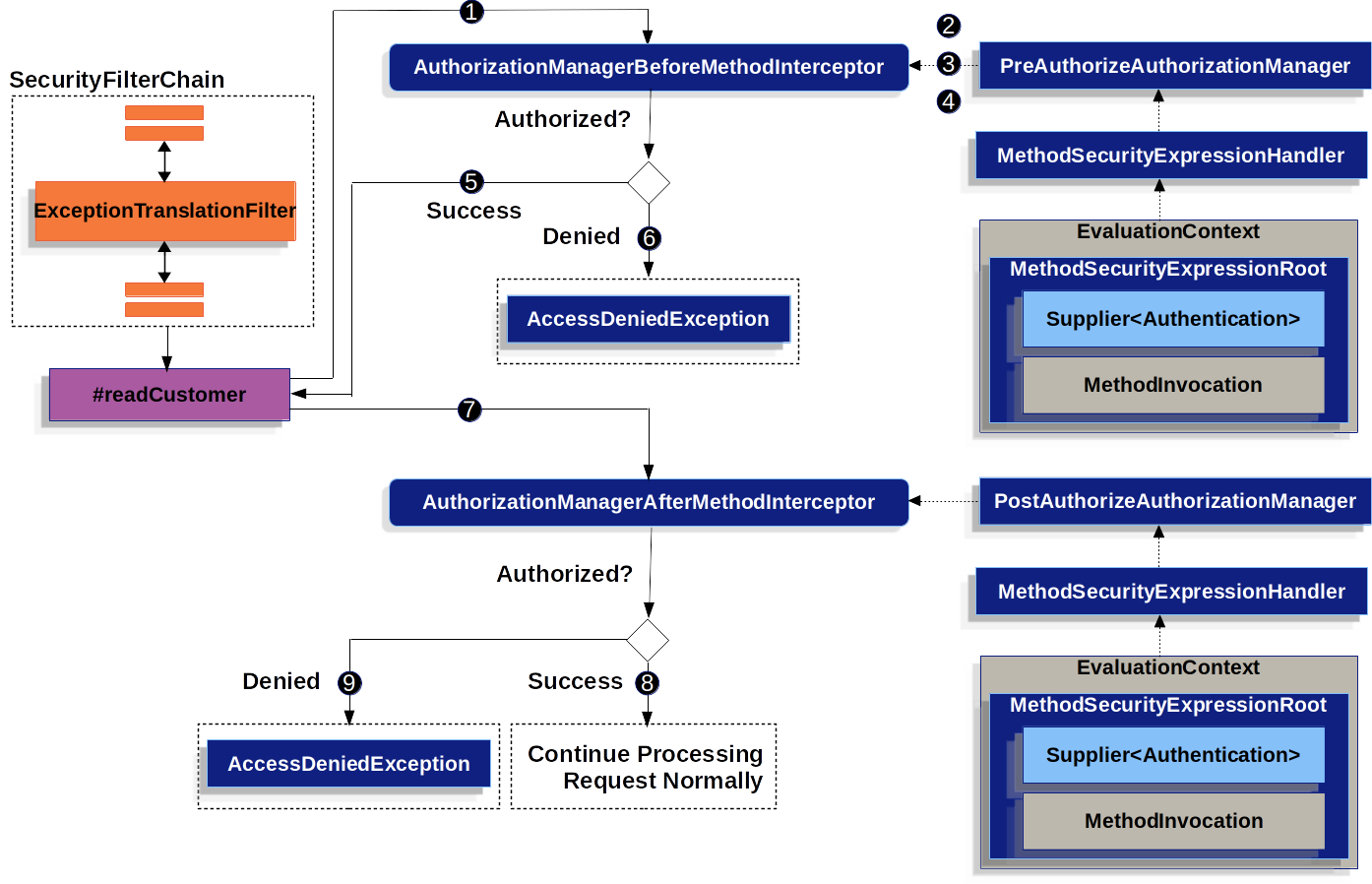
-
Spring AOP 调用其代理方法 。在代理的其他顾问中,它调用与
@PreAuthorize切入点匹配的AuthorizationManagerBeforeMethodInterceptorreadCustomer -
授权管理器使用 a 来解析注释的 SPEL 表达式,并从 a 构造一个包含
Supplier<Authentication>和 的对应 a。MethodSecurityExpressionHandlerEvaluationContextMethodSecurityExpressionRootMethodInvocation -
侦听器使用此上下文来评估表达式;具体来说,它从 中读取
Authentication,并检查它是否在其权限集合中具有Supplierpermission:read -
如果评估通过,则 Spring AOP 将继续调用该方法。
-
否则,拦截器将发布一个并抛出一个
AccessDeniedException,ExceptionTranslationFilter捕获该异常,并向响应返回一个 403 状态码AuthorizationDeniedEvent -
在方法返回后, Spring AOP 调用一个与
@PostAuthorize切入点匹配的AuthorizationManagerAfterMethodInterceptor,操作与上述相同,但使用PostAuthorizeAuthorizationManager -
如果评估通过(在本例中,返回值属于已登录用户),则处理将继续正常进行
-
如果不是,则拦截器发布一个并抛出一个
AccessDeniedException,ExceptionTranslationFilter捕获该异常并向响应返回 403 状态码AuthorizationDeniedEvent
如果该方法未在 HTTP 请求的上下文中调用,则可能需要自行处理AccessDeniedException |
多个注释是按顺序计算的
如上所述,如果方法调用涉及多个 Method Security 注释,则一次处理一个 Method Security 注释。 这意味着它们可以统称为“和”在一起。 换句话说,要使调用获得授权,所有 Comments 检查都需要通过授权。
每个注释都有自己的切入点
每个 Annotation 都有自己的 pointcut 实例,该实例从方法及其封闭类开始,在整个对象层次结构中查找该 Annotation 或其元 Annotation 对应项。
每个 Annotation 都有自己的 Method Interceptor
每个 Comments 都有其自己的专用方法拦截器。
这样做的原因是为了让事情更具可组合性。
例如,如果需要,您可以禁用 Spring Security 默认值并仅发布 @PostAuthorize 方法拦截器。
方法拦截器如下:
-
对于
@PreAuthorize,SpringSecurity 使用AuthorizationManagerBeforeMethodInterceptor#preAuthorize,而后者又使用PreAuthorizeAuthorizationManager -
对于
@PostAuthorize,SpringSecurity 使用AuthorizationManagerAfterMethodInterceptor#postAuthorize,而后者又使用PostAuthorizeAuthorizationManager -
对于
@PreFilter,SpringSecurity 使用PreFilterAuthorizationMethodInterceptor -
对于
@PostFilter,SpringSecurity 使用PostFilterAuthorizationMethodInterceptor -
对于
@Secured,SpringSecurity 使用AuthorizationManagerBeforeMethodInterceptor#secured,而后者又使用SecuredAuthorizationManager -
对于 JSR-250 注释,Spring Security 使用
AuthorizationManagerBeforeMethodInterceptor#jsr250,而后者又使用Jsr250AuthorizationManager
一般来说,当您添加时,您可以考虑以下列表作为 Spring Security 发布的拦截器的代表:@EnableMethodSecurity
-
Java
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
static Advisor preAuthorizeMethodInterceptor() {
return AuthorizationManagerBeforeMethodInterceptor.preAuthorize();
}
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
static Advisor postAuthorizeMethodInterceptor() {
return AuthorizationManagerAfterMethodInterceptor.postAuthorize();
}
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
static Advisor preFilterMethodInterceptor() {
return AuthorizationManagerBeforeMethodInterceptor.preFilter();
}
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
static Advisor postFilterMethodInterceptor() {
return AuthorizationManagerAfterMethodInterceptor.postFilter();
}优先授予对复杂 SPEL 表达式的权限
很多时候,引入复杂的 SPEL 表达式可能很诱人,如下所示:
-
Java
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('permission:read') || hasRole('ADMIN')")@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('permission:read') || hasRole('ADMIN')")但是,您可以改为授予具有 .
一种方法是使用这样的:permission:readROLE_ADMINRoleHierarchy
-
Java
-
Kotlin
-
Xml
@Bean
static RoleHierarchy roleHierarchy() {
return RoleHierarchyImpl.fromHierarchy("ROLE_ADMIN > permission:read");
}companion object {
@Bean
fun roleHierarchy(): RoleHierarchy {
return RoleHierarchyImpl.fromHierarchy("ROLE_ADMIN > permission:read")
}
}<bean id="roleHierarchy"
class="org.springframework.security.access.hierarchicalroles.RoleHierarchyImpl" factory-method="fromHierarchy">
<constructor-arg value="ROLE_ADMIN > permission:read"/>
</bean>然后在 MethodSecurityExpressionHandler 实例中设置它。
然后,这允许你有一个更简单的 @PreAuthorize 表达式,如下所示:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('permission:read')")@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('permission:read')")或者,在可能的情况下,在登录时将特定于应用程序的授权逻辑调整为授予的权限。
比较请求级和方法级授权
何时应优先使用方法级授权而不是请求级授权? 其中一些归结为品味;但是,请考虑以下每个优势列表来帮助您做出决定。
请求级别 |
方法级别 |
|
授权类型 |
粗粒度 |
细粒度 |
配置位置 |
在 Config 类中声明 |
local to 方法声明 |
配置样式 |
DSL (英语) |
附注 |
授权定义 |
编程 |
斯佩尔 |
主要的权衡似乎是您希望授权规则所在的位置。
请务必记住,当您使用基于注释的方法安全性时,未注释的方法将不安全。
为了防止这种情况,请在 HttpSecurity 实例中声明一个 catch-all 授权规则。 |
使用注释进行授权
Spring Security 启用方法级授权支持的主要方式是通过可以添加到方法、类和接口的 Comments。
授权方法调用@PreAuthorize
当 Method Security 处于活动状态时,您可以使用 @PreAuthorize 注释对方法进行注释,如下所示:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Component
public class BankService {
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')")
public Account readAccount(Long id) {
// ... is only invoked if the `Authentication` has the `ROLE_ADMIN` authority
}
}@Component
open class BankService {
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')")
fun readAccount(val id: Long): Account {
// ... is only invoked if the `Authentication` has the `ROLE_ADMIN` authority
}
}这是为了指示只有在提供的表达式通过时才能调用该方法。hasRole('ADMIN')
然后,您可以测试该类以确认它正在强制执行授权规则,如下所示:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Autowired
BankService bankService;
@WithMockUser(roles="ADMIN")
@Test
void readAccountWithAdminRoleThenInvokes() {
Account account = this.bankService.readAccount("12345678");
// ... assertions
}
@WithMockUser(roles="WRONG")
@Test
void readAccountWithWrongRoleThenAccessDenied() {
assertThatExceptionOfType(AccessDeniedException.class).isThrownBy(
() -> this.bankService.readAccount("12345678"));
}@WithMockUser(roles="ADMIN")
@Test
fun readAccountWithAdminRoleThenInvokes() {
val account: Account = this.bankService.readAccount("12345678")
// ... assertions
}
@WithMockUser(roles="WRONG")
@Test
fun readAccountWithWrongRoleThenAccessDenied() {
assertThatExceptionOfType(AccessDeniedException::class.java).isThrownBy {
this.bankService.readAccount("12345678")
}
}
@PreAuthorize也可以是元注释,在类或接口级别定义,并使用 SPEL 授权表达式。 |
虽然对于声明所需的权限非常有帮助,但它也可以用于评估涉及方法参数的更复杂的表达式。@PreAuthorize
授权方法结果@PostAuthorize
当 Method Security 处于活动状态时,您可以使用 @PostAuthorize 注释对方法进行注释,如下所示:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Component
public class BankService {
@PostAuthorize("returnObject.owner == authentication.name")
public Account readAccount(Long id) {
// ... is only returned if the `Account` belongs to the logged in user
}
}@Component
open class BankService {
@PostAuthorize("returnObject.owner == authentication.name")
fun readAccount(val id: Long): Account {
// ... is only returned if the `Account` belongs to the logged in user
}
}这是为了指示该方法只有在提供的表达式通过时才能返回值。 表示要返回的对象。returnObject.owner == authentication.namereturnObjectAccount
然后,您可以测试该类以确认它正在强制执行授权规则:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Autowired
BankService bankService;
@WithMockUser(username="owner")
@Test
void readAccountWhenOwnedThenReturns() {
Account account = this.bankService.readAccount("12345678");
// ... assertions
}
@WithMockUser(username="wrong")
@Test
void readAccountWhenNotOwnedThenAccessDenied() {
assertThatExceptionOfType(AccessDeniedException.class).isThrownBy(
() -> this.bankService.readAccount("12345678"));
}@WithMockUser(username="owner")
@Test
fun readAccountWhenOwnedThenReturns() {
val account: Account = this.bankService.readAccount("12345678")
// ... assertions
}
@WithMockUser(username="wrong")
@Test
fun readAccountWhenNotOwnedThenAccessDenied() {
assertThatExceptionOfType(AccessDeniedException::class.java).isThrownBy {
this.bankService.readAccount("12345678")
}
}
@PostAuthorize也可以是元注释,在类或接口级别定义,并使用 SPEL 授权表达式。 |
@PostAuthorize在防御不安全的 Direct Object Reference 时特别有用。
事实上,它可以被定义为元注释,如下所示:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Target({ ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@PostAuthorize("returnObject.owner == authentication.name")
public @interface RequireOwnership {}@Target(ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@PostAuthorize("returnObject.owner == authentication.name")
annotation class RequireOwnership允许您改为按以下方式对服务进行注释:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Component
public class BankService {
@RequireOwnership
public Account readAccount(Long id) {
// ... is only returned if the `Account` belongs to the logged in user
}
}@Component
open class BankService {
@RequireOwnership
fun readAccount(val id: Long): Account {
// ... is only returned if the `Account` belongs to the logged in user
}
}结果是,上述方法仅在其属性与已登录用户的 .
如果没有,Spring Security 将抛出一个并返回一个 403 状态代码。AccountownernameAccessDeniedException
过滤方法参数@PreFilter
当 Method Security 处于活动状态时,您可以使用 @PreFilter 注释对方法进行注释,如下所示:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Component
public class BankService {
@PreFilter("filterObject.owner == authentication.name")
public Collection<Account> updateAccounts(Account... accounts) {
// ... `accounts` will only contain the accounts owned by the logged-in user
return updated;
}
}@Component
open class BankService {
@PreFilter("filterObject.owner == authentication.name")
fun updateAccounts(vararg accounts: Account): Collection<Account> {
// ... `accounts` will only contain the accounts owned by the logged-in user
return updated
}
}这是为了从表达式失败的地方过滤掉任何值。 表示每个 IN,并用于测试每个 。accountsfilterObject.owner == authentication.namefilterObjectaccountaccountsaccount
然后,您可以通过以下方式测试该类,以确认它正在强制执行授权规则:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Autowired
BankService bankService;
@WithMockUser(username="owner")
@Test
void updateAccountsWhenOwnedThenReturns() {
Account ownedBy = ...
Account notOwnedBy = ...
Collection<Account> updated = this.bankService.updateAccounts(ownedBy, notOwnedBy);
assertThat(updated).containsOnly(ownedBy);
}@Autowired
lateinit var bankService: BankService
@WithMockUser(username="owner")
@Test
fun updateAccountsWhenOwnedThenReturns() {
val ownedBy: Account = ...
val notOwnedBy: Account = ...
val updated: Collection<Account> = bankService.updateAccounts(ownedBy, notOwnedBy)
assertThat(updated).containsOnly(ownedBy)
}
@PreFilter也可以是元注释,在类或接口级别定义,并使用 SPEL 授权表达式。 |
@PreFilter支持数组、集合、映射和流(只要流仍处于打开状态)。
例如,上述声明的功能与以下其他四个声明相同:updateAccounts
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@PreFilter("filterObject.owner == authentication.name")
public Collection<Account> updateAccounts(Account[] accounts)
@PreFilter("filterObject.owner == authentication.name")
public Collection<Account> updateAccounts(Collection<Account> accounts)
@PreFilter("filterObject.value.owner == authentication.name")
public Collection<Account> updateAccounts(Map<String, Account> accounts)
@PreFilter("filterObject.owner == authentication.name")
public Collection<Account> updateAccounts(Stream<Account> accounts)@PreFilter("filterObject.owner == authentication.name")
fun updateAccounts(accounts: Array<Account>): Collection<Account>
@PreFilter("filterObject.owner == authentication.name")
fun updateAccounts(accounts: Collection<Account>): Collection<Account>
@PreFilter("filterObject.value.owner == authentication.name")
fun updateAccounts(accounts: Map<String, Account>): Collection<Account>
@PreFilter("filterObject.owner == authentication.name")
fun updateAccounts(accounts: Stream<Account>): Collection<Account>结果是,上述方法将仅包含其属性与已登录用户的 .Accountownername
过滤方法结果与@PostFilter
当 Method Security 处于活动状态时,您可以使用 @PostFilter 注释对方法进行注释,如下所示:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Component
public class BankService {
@PostFilter("filterObject.owner == authentication.name")
public Collection<Account> readAccounts(String... ids) {
// ... the return value will be filtered to only contain the accounts owned by the logged-in user
return accounts;
}
}@Component
open class BankService {
@PreFilter("filterObject.owner == authentication.name")
fun readAccounts(vararg ids: String): Collection<Account> {
// ... the return value will be filtered to only contain the accounts owned by the logged-in user
return accounts
}
}这是为了从表达式失败的返回值中筛选出任何值。 表示每个 IN,并用于测试每个 。filterObject.owner == authentication.namefilterObjectaccountaccountsaccount
然后,您可以像这样测试该类,以确认它正在强制执行授权规则:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Autowired
BankService bankService;
@WithMockUser(username="owner")
@Test
void readAccountsWhenOwnedThenReturns() {
Collection<Account> accounts = this.bankService.updateAccounts("owner", "not-owner");
assertThat(accounts).hasSize(1);
assertThat(accounts.get(0).getOwner()).isEqualTo("owner");
}@Autowired
lateinit var bankService: BankService
@WithMockUser(username="owner")
@Test
fun readAccountsWhenOwnedThenReturns() {
val accounts: Collection<Account> = bankService.updateAccounts("owner", "not-owner")
assertThat(accounts).hasSize(1)
assertThat(accounts[0].owner).isEqualTo("owner")
}
@PostFilter也可以是元注释,在类或接口级别定义,并使用 SPEL 授权表达式。 |
@PostFilter支持数组、集合、映射和流(只要流仍处于打开状态)。
例如,上述声明的功能与其他三个声明相同:readAccounts
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@PostFilter("filterObject.owner == authentication.name")
public Collection<Account> readAccounts(String... ids)
@PostFilter("filterObject.owner == authentication.name")
public Account[] readAccounts(String... ids)
@PostFilter("filterObject.value.owner == authentication.name")
public Map<String, Account> readAccounts(String... ids)
@PostFilter("filterObject.owner == authentication.name")
public Stream<Account> readAccounts(String... ids)@PostFilter("filterObject.owner == authentication.name")
fun readAccounts(vararg ids: String): Collection<Account>
@PostFilter("filterObject.owner == authentication.name")
fun readAccounts(vararg ids: String): Array<Account>
@PostFilter("filterObject.owner == authentication.name")
fun readAccounts(vararg ids: String): Map<String, Account>
@PostFilter("filterObject.owner == authentication.name")
fun readAccounts(vararg ids: String): Stream<Account>结果是,上述方法将返回其属性与已登录用户的 .Accountownername
| 内存筛选显然可能很昂贵,因此要考虑是否更适合筛选数据层中的数据。 |
授权方法调用@Secured
@Secured 是用于授权调用的旧选项。@PreAuthorize 取代它,而是推荐使用。
要使用 Comments,您应该首先更改 Method Security 声明以启用它,如下所示:@Secured
-
Java
-
Kotlin
-
Xml
@EnableMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true)@EnableMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true)<sec:method-security secured-enabled="true"/>这将导致 Spring Security 发布相应的方法拦截器,该拦截器授权用 Comments .@Secured
使用 JSR-250 注释授权方法调用
如果您想使用 JSR-250 注释,Spring Security 也支持它。@PreAuthorize 具有更强的表现力,因此推荐使用。
要使用 JSR-250 注释,您应该首先更改 Method Security 声明以启用它们,如下所示:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
-
Xml
@EnableMethodSecurity(jsr250Enabled = true)@EnableMethodSecurity(jsr250Enabled = true)<sec:method-security jsr250-enabled="true"/>这将导致 Spring Security 发布相应的方法拦截器,该拦截器授权用 、 、 和 和 注释的方法、类和接口。@RolesAllowed@PermitAll@DenyAll
在类或接口级别声明注释
还支持在类和接口级别具有 Method Security 注释。
如果它是在类级别,如下所示:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Controller
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('ROLE_USER')")
public class MyController {
@GetMapping("/endpoint")
public String endpoint() { ... }
}@Controller
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('ROLE_USER')")
open class MyController {
@GetMapping("/endpoint")
fun endpoint(): String { ... }
}然后,所有方法都继承类级行为。
或者,如果它在类和方法级别都声明如下:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Controller
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('ROLE_USER')")
public class MyController {
@GetMapping("/endpoint")
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('ROLE_ADMIN')")
public String endpoint() { ... }
}@Controller
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('ROLE_USER')")
open class MyController {
@GetMapping("/endpoint")
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('ROLE_ADMIN')")
fun endpoint(): String { ... }
}然后,声明 Comments 的方法将覆盖类级 Comments。
接口也是如此,不同之处在于,如果一个类从两个不同的接口继承 Comments,则启动将失败。 这是因为 Spring Security 无法判断你想使用哪一个。
在这种情况下,您可以通过将 Annotation 添加到具体方法来解决歧义。
使用 Meta 注释
Method Security 支持元注释。 这意味着您可以采用任何注释,并根据特定于应用程序的用例提高可读性。
例如,您可以简化为:@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')")@IsAdmin
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Target({ ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')")
public @interface IsAdmin {}@Target(ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')")
annotation class IsAdmin结果是,您现在可以在安全方法上执行以下操作:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Component
public class BankService {
@IsAdmin
public Account readAccount(Long id) {
// ... is only returned if the `Account` belongs to the logged in user
}
}@Component
open class BankService {
@IsAdmin
fun readAccount(val id: Long): Account {
// ... is only returned if the `Account` belongs to the logged in user
}
}这将产生更具可读性的方法定义。
模板化元注释表达式
您还可以选择使用元注释模板,它允许使用更强大的注释定义。
首先,发布以下 Bean:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Bean
static AnnotationTemplateExpressionDefaults templateExpressionDefaults() {
return new AnnotationTemplateExpressionDefaults();
}companion object {
@Bean
fun templateExpressionDefaults(): AnnotationTemplateExpressionDefaults {
return AnnotationTemplateExpressionDefaults()
}
}现在,您可以创建更强大的内容,而不是 ,如下所示:@IsAdmin@HasRole
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Target({ ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('{value}')")
public @interface HasRole {
String value();
}@Target(ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('{value}')")
annotation class HasRole(val value: String)结果是,您现在可以在安全方法上执行以下操作:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Component
public class BankService {
@HasRole("ADMIN")
public Account readAccount(Long id) {
// ... is only returned if the `Account` belongs to the logged in user
}
}@Component
open class BankService {
@HasRole("ADMIN")
fun readAccount(val id: Long): Account {
// ... is only returned if the `Account` belongs to the logged in user
}
}请注意,这也适用于方法变量和所有 Comments 类型,尽管您需要小心地正确使用引号,以便生成的 SPEL 表达式是正确的。
例如,请考虑以下注释:@HasAnyRole
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Target({ ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@PreAuthorize("hasAnyRole({roles})")
public @interface HasAnyRole {
String[] roles();
}@Target(ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@PreAuthorize("hasAnyRole({roles})")
annotation class HasAnyRole(val roles: Array<String>)在这种情况下,您会注意到您不应该在表达式中使用引号,而应该在参数值中使用引号,如下所示:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Component
public class BankService {
@HasAnyRole(roles = { "'USER'", "'ADMIN'" })
public Account readAccount(Long id) {
// ... is only returned if the `Account` belongs to the logged in user
}
}@Component
open class BankService {
@HasAnyRole(roles = arrayOf("'USER'", "'ADMIN'"))
fun readAccount(val id: Long): Account {
// ... is only returned if the `Account` belongs to the logged in user
}
}因此,一旦替换,表达式就会变为 。@PreAuthorize("hasAnyRole('USER', 'ADMIN')")
启用某些注释
您可以关闭 的预配置,并将其替换为您自己的预配置。
如果要自定义 AuthorizationManager 或 .
或者,您可能只想启用特定批注,例如 .@EnableMethodSecurityPointcut@PostAuthorize
您可以通过以下方式执行此操作:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
-
Xml
@Configuration
@EnableMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = false)
class MethodSecurityConfig {
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
Advisor postAuthorize() {
return AuthorizationManagerAfterMethodInterceptor.postAuthorize();
}
}@Configuration
@EnableMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = false)
class MethodSecurityConfig {
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
fun postAuthorize() : Advisor {
return AuthorizationManagerAfterMethodInterceptor.postAuthorize()
}
}<sec:method-security pre-post-enabled="false"/>
<aop:config/>
<bean id="postAuthorize"
class="org.springframework.security.authorization.method.AuthorizationManagerBeforeMethodInterceptor"
factory-method="postAuthorize"/>上面的代码片段通过首先禁用 Method Security 的预配置,然后发布 @PostAuthorize 拦截器本身来实现这一点。
授权方式<intercept-methods>
虽然使用 Spring Security 的基于 Comments 的支持是方法安全性的首选,但您也可以使用 XML 来声明 Bean 授权规则。
如果需要在 XML 配置中声明它,可以使用 <intercept-methods>,如下所示:
-
Xml
<bean class="org.mycompany.MyController">
<intercept-methods>
<protect method="get*" access="hasAuthority('read')"/>
<protect method="*" access="hasAuthority('write')"/>
</intercept-methods>
</bean>| 这仅支持按前缀或按名称匹配方法。 如果您的需求比这更复杂,请改用 annotation support。 |
以编程方式授权方法
如您所见,有几种方法可以使用方法安全性 SPEL 表达式指定重要的授权规则。
有多种方法可以让你的逻辑基于 Java 而不是基于 SPEL。 这为整个 Java 语言提供了 use 访问权限,以提高可测试性和流控制。
在 SPEL 中使用自定义 Bean
以编程方式授权方法的第一种方法是一个两步过程。
首先,声明一个 bean,该 bean 具有一个采用如下所示的实例的方法:MethodSecurityExpressionOperations
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Component("authz")
public class AuthorizationLogic {
public boolean decide(MethodSecurityExpressionOperations operations) {
// ... authorization logic
}
}@Component("authz")
open class AuthorizationLogic {
fun decide(val operations: MethodSecurityExpressionOperations): boolean {
// ... authorization logic
}
}然后,按以下方式在 Comments 中引用该 bean:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Controller
public class MyController {
@PreAuthorize("@authz.decide(#root)")
@GetMapping("/endpoint")
public String endpoint() {
// ...
}
}@Controller
open class MyController {
@PreAuthorize("@authz.decide(#root)")
@GetMapping("/endpoint")
fun String endpoint() {
// ...
}
}Spring Security 将为每个方法调用在该 bean 上调用给定的方法。
这样做的好处是,您的所有授权逻辑都位于一个单独的类中,该类可以独立进行单元测试和正确性验证。 它还可以访问完整的 Java 语言。
除了返回 a 之外,您还可以返回以指示代码放弃做出决策。Booleannull |
如果要包含有关决策性质的更多信息,可以改为返回如下所示的自定义:AuthorizationDecision
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Component("authz")
public class AuthorizationLogic {
public AuthorizationDecision decide(MethodSecurityExpressionOperations operations) {
// ... authorization logic
return new MyAuthorizationDecision(false, details);
}
}@Component("authz")
open class AuthorizationLogic {
fun decide(val operations: MethodSecurityExpressionOperations): AuthorizationDecision {
// ... authorization logic
return MyAuthorizationDecision(false, details)
}
}或者抛出一个自定义实例。
但请注意,返回对象是首选,因为这不会产生生成堆栈跟踪的费用。AuthorizationDeniedException
然后,您可以在自定义授权结果的处理方式时访问自定义详细信息。
使用自定义授权管理器
以编程方式授权方法的第二种方法是创建自定义 AuthorizationManager。
首先,声明一个授权 Management 器实例,可能像这样:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Component
public class MyAuthorizationManager implements AuthorizationManager<MethodInvocation>, AuthorizationManager<MethodInvocationResult> {
@Override
public AuthorizationDecision check(Supplier<Authentication> authentication, MethodInvocation invocation) {
// ... authorization logic
}
@Override
public AuthorizationDecision check(Supplier<Authentication> authentication, MethodInvocationResult invocation) {
// ... authorization logic
}
}@Component
class MyAuthorizationManager : AuthorizationManager<MethodInvocation>, AuthorizationManager<MethodInvocationResult> {
override fun check(authentication: Supplier<Authentication>, invocation: MethodInvocation): AuthorizationDecision {
// ... authorization logic
}
override fun check(authentication: Supplier<Authentication>, invocation: MethodInvocationResult): AuthorizationDecision {
// ... authorization logic
}
}然后,使用与您希望它运行的时间相对应的切入点发布方法 interceptor。
例如,你可以将 how 和 work 替换为:AuthorizationManager@PreAuthorize@PostAuthorize
-
Java
-
Kotlin
-
Xml
@Configuration
@EnableMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = false)
class MethodSecurityConfig {
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
Advisor preAuthorize(MyAuthorizationManager manager) {
return AuthorizationManagerBeforeMethodInterceptor.preAuthorize(manager);
}
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
Advisor postAuthorize(MyAuthorizationManager manager) {
return AuthorizationManagerAfterMethodInterceptor.postAuthorize(manager);
}
}@Configuration
@EnableMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = false)
class MethodSecurityConfig {
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
fun preAuthorize(val manager: MyAuthorizationManager) : Advisor {
return AuthorizationManagerBeforeMethodInterceptor.preAuthorize(manager)
}
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
fun postAuthorize(val manager: MyAuthorizationManager) : Advisor {
return AuthorizationManagerAfterMethodInterceptor.postAuthorize(manager)
}
}<sec:method-security pre-post-enabled="false"/>
<aop:config/>
<bean id="preAuthorize"
class="org.springframework.security.authorization.method.AuthorizationManagerBeforeMethodInterceptor"
factory-method="preAuthorize">
<constructor-arg ref="myAuthorizationManager"/>
</bean>
<bean id="postAuthorize"
class="org.springframework.security.authorization.method.AuthorizationManagerAfterMethodInterceptor"
factory-method="postAuthorize">
<constructor-arg ref="myAuthorizationManager"/>
</bean>|
您可以使用中指定的 order 常量将拦截器放置在 Spring Security 方法拦截器之间。 |
自定义表达式处理
或者,第三种,您可以自定义每个 SPEL 表达式的处理方式。
为此,您可以公开自定义 MethodSecurityExpressionHandler,如下所示:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
-
Xml
@Bean
static MethodSecurityExpressionHandler methodSecurityExpressionHandler(RoleHierarchy roleHierarchy) {
DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandler handler = new DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandler();
handler.setRoleHierarchy(roleHierarchy);
return handler;
}companion object {
@Bean
fun methodSecurityExpressionHandler(val roleHierarchy: RoleHierarchy) : MethodSecurityExpressionHandler {
val handler = DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandler()
handler.setRoleHierarchy(roleHierarchy)
return handler
}
}<sec:method-security>
<sec:expression-handler ref="myExpressionHandler"/>
</sec:method-security>
<bean id="myExpressionHandler"
class="org.springframework.security.messaging.access.expression.DefaultMessageSecurityExpressionHandler">
<property name="roleHierarchy" ref="roleHierarchy"/>
</bean>|
我们使用方法公开,以确保 Spring 在初始化 Spring Security 的方法安全类之前发布它 |
你还可以子类DefaultMessageSecurityExpressionHandler,以添加超出默认值的自定义授权表达式。
使用 AOT
Spring Security 将扫描应用程序上下文中的所有 bean 以查找使用 或 的方法。
找到一个 bean 后,它将解析安全表达式中使用的任何 bean,并为该 bean 注册适当的运行时提示。
如果找到使用 的方法,它将在方法的返回类型 for 和 annotations 中递归搜索并相应地注册它们。@PreAuthorize@PostAuthorize@AuthorizeReturnObject@PreAuthorize@PostAuthorize
例如,考虑以下 Spring Boot 应用程序:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Service
public class AccountService { (1)
@PreAuthorize("@authz.decide()") (2)
@AuthorizeReturnObject (3)
public Account getAccountById(String accountId) {
// ...
}
}
public class Account {
private final String accountNumber;
// ...
@PreAuthorize("@accountAuthz.canViewAccountNumber()") (4)
public String getAccountNumber() {
return this.accountNumber;
}
@AuthorizeReturnObject (5)
public User getUser() {
return new User("John Doe");
}
}
public class User {
private final String fullName;
// ...
@PostAuthorize("@myOtherAuthz.decide()") (6)
public String getFullName() {
return this.fullName;
}
}@Service
class AccountService { (1)
@PreAuthorize("@authz.decide()") (2)
@AuthorizeReturnObject (3)
fun getAccountById(accountId: String): Account {
// ...
}
}
class Account(private val accountNumber: String) {
@PreAuthorize("@accountAuthz.canViewAccountNumber()") (4)
fun getAccountNumber(): String {
return this.accountNumber
}
@AuthorizeReturnObject (5)
fun getUser(): User {
return User("John Doe")
}
}
class User(private val fullName: String) {
@PostAuthorize("@myOtherAuthz.decide()") (6)
fun getFullName(): String {
return this.fullName
}
}| 1 | Spring Security 找到 beanAccountService |
| 2 | 找到一个使用 的方法,它将解析表达式中使用的任何 bean 名称(在这种情况下),并为 bean 类注册运行时提示@PreAuthorizeauthz |
| 3 | 查找使用 的方法,它将查看该方法的返回类型 any 或@AuthorizeReturnObject@PreAuthorize@PostAuthorize |
| 4 | 然后,它找到具有另一个 bean 名称的 a: ;运行时提示也为 Bean 类注册@PreAuthorizeaccountAuthz |
| 5 | 找到另一个 IT 部门后,它将再次查看该方法的返回类型@AuthorizeReturnObject |
| 6 | 现在,发现 a 还使用了另一个 bean 名称:;运行时提示也为 Bean 类注册@PostAuthorizemyOtherAuthz |
很多时候 Spring Security 无法提前确定方法的实际返回类型,因为它可能隐藏在擦除的泛型类型中。
请考虑以下服务:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Service
public class AccountService {
@AuthorizeReturnObject
public List<Account> getAllAccounts() {
// ...
}
}@Service
class AccountService {
@AuthorizeReturnObject
fun getAllAccounts(): List<Account> {
// ...
}
}在这种情况下,泛型类型被擦除,因此 Spring Security 事先并不明显需要访问它以检查 和 。Account@PreAuthorize@PostAuthorize
要解决此问题,您可以发布 PrePostAuthorizeExpressionBeanHintsRegistrar,如下所示:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
static SecurityHintsRegistrar registerTheseToo() {
return new PrePostAuthorizeExpressionBeanHintsRegistrar(Account.class);
}@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
fun registerTheseToo(): SecurityHintsRegistrar {
return PrePostAuthorizeExpressionBeanHintsRegistrar(Account::class.java)
}使用 AspectJ 进行授权
使用自定义切入点匹配方法
由于 Spring AOP 构建,您可以声明与 Comments 无关的模式,类似于请求级授权。 这具有集中方法级授权规则的潜在优势。
例如,您可以使用 publish your own 或使用 <protect-pointcut> 将 AOP 表达式与服务层的授权规则匹配,如下所示:Advisor
-
Java
-
Kotlin
-
Xml
import static org.springframework.security.authorization.AuthorityAuthorizationManager.hasRole
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
static Advisor protectServicePointcut() {
AspectJExpressionPointcut pattern = new AspectJExpressionPointcut()
pattern.setExpression("execution(* com.mycompany.*Service.*(..))")
return new AuthorizationManagerBeforeMethodInterceptor(pattern, hasRole("USER"))
}import static org.springframework.security.authorization.AuthorityAuthorizationManager.hasRole
companion object {
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
fun protectServicePointcut(): Advisor {
val pattern = AspectJExpressionPointcut()
pattern.setExpression("execution(* com.mycompany.*Service.*(..))")
return new AuthorizationManagerBeforeMethodInterceptor(pattern, hasRole("USER"))
}
}<sec:method-security>
<protect-pointcut expression="execution(* com.mycompany.*Service.*(..))" access="hasRole('USER')"/>
</sec:method-security>与 AspectJ Byte-waving 集成
有时可以通过使用 AspectJ 将 Spring Security 建议编织到 bean 的字节码中来提高性能。
在设置了 AspectJ 之后,你可以非常简单地在注解或元素中声明你正在使用 AspectJ:@EnableMethodSecurity<method-security>
-
Java
-
Kotlin
-
Xml
@EnableMethodSecurity(mode=AdviceMode.ASPECTJ)@EnableMethodSecurity(mode=AdviceMode.ASPECTJ)<sec:method-security mode="aspectj"/>结果将是 Spring Security 将其顾问作为 AspectJ 建议发布,以便它们可以相应地被编织进来。
指定顺序
如前所述,每个注解都有一个 Spring AOP 方法拦截器,每个注解在 Spring AOP advisor 链中都有一个位置。
即,方法 interceptor's order 是 100,'s 是 200,依此类推。@PreFilter@PreAuthorize
需要注意的原因是,还有其他基于 AOP 的注解,例如 ,它们的 order 为 .
换句话说,默认情况下,它们位于 advisor 链的末尾。@EnableTransactionManagementInteger.MAX_VALUE
有时,在 Spring Security 之前执行其他建议可能很有价值。
例如,如果您有一个带有 and 注释的方法,您可能希望事务在运行时仍处于打开状态,以便 an 将导致回滚。@Transactional@PostAuthorize@PostAuthorizeAccessDeniedException
要在方法授权建议运行之前打开交易,您可以像这样设置 'order:@EnableTransactionManagement@EnableTransactionManagement
-
Java
-
Kotlin
-
Xml
@EnableTransactionManagement(order = 0)@EnableTransactionManagement(order = 0)<tx:annotation-driven ref="txManager" order="0"/>由于最早的方法拦截器()被设置为 100 的顺序,因此设置为零意味着事务通知将在所有 Spring Security 通知之前运行。@PreFilter
使用 SPEL 表示授权
您已经看到了几个使用 SpEL 的示例,现在让我们更深入地介绍 API。
Spring Security 将其所有授权字段和方法封装在一组根对象中。
最通用的根对象称为 ,它构成了 的基础。
Spring Security 在准备评估授权表达式时提供此根对象。SecurityExpressionRootMethodSecurityExpressionRootMethodSecurityEvaluationContext
使用授权表达式字段和方法
它提供的第一件事是 SPEL 表达式的一组增强的授权字段和方法。 以下是最常见方法的快速概述:
-
permitAll- 该方法不需要授权即可调用;请注意,在这种情况下,永远不会从会话中检索Authentication -
denyAll- 该方法在任何情况下都是不允许的;请注意,在这种情况下,永远不会从会话中检索Authentication -
hasAuthority- 该方法要求 具有与给定值匹配的GrantedAuthorityAuthentication -
hasRole- 该前缀的快捷方式或配置为默认前缀的任何内容hasAuthorityROLE_ -
hasAnyAuthority- 该方法要求 have a 匹配任何给定值AuthenticationGrantedAuthority -
hasAnyRole- 该前缀的快捷方式或配置为默认前缀的任何内容hasAnyAuthorityROLE_ -
hasPermission- 实例中的钩子,用于执行对象级授权PermissionEvaluator
以下是最常见的字段的简要介绍:
-
authentication- 与此方法调用关联的实例Authentication -
principal- 与此方法调用关联的Authentication#getPrincipal
现在,您已经了解了模式、规则以及如何将它们配对在一起,您应该能够理解这个更复杂的示例中发生了什么:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
-
Xml
@Component
public class MyService {
@PreAuthorize("denyAll") (1)
MyResource myDeprecatedMethod(...);
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')") (2)
MyResource writeResource(...)
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('db') and hasRole('ADMIN')") (3)
MyResource deleteResource(...)
@PreAuthorize("principal.claims['aud'] == 'my-audience'") (4)
MyResource readResource(...);
@PreAuthorize("@authz.check(authentication, #root)")
MyResource shareResource(...);
}@Component
open class MyService {
@PreAuthorize("denyAll") (1)
fun myDeprecatedMethod(...): MyResource
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')") (2)
fun writeResource(...): MyResource
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('db') and hasRole('ADMIN')") (3)
fun deleteResource(...): MyResource
@PreAuthorize("principal.claims['aud'] == 'my-audience'") (4)
fun readResource(...): MyResource
@PreAuthorize("@authz.check(#root)")
fun shareResource(...): MyResource
}<sec:method-security>
<protect-pointcut expression="execution(* com.mycompany.*Service.myDeprecatedMethod(..))" access="denyAll"/> (1)
<protect-pointcut expression="execution(* com.mycompany.*Service.writeResource(..))" access="hasRole('ADMIN')"/> (2)
<protect-pointcut expression="execution(* com.mycompany.*Service.deleteResource(..))" access="hasAuthority('db') and hasRole('ADMIN')"/> (3)
<protect-pointcut expression="execution(* com.mycompany.*Service.readResource(..))" access="principal.claims['aud'] == 'my-audience'"/> (4)
<protect-pointcut expression="execution(* com.mycompany.*Service.shareResource(..))" access="@authz.check(#root)"/> (5)
</sec:method-security>| 1 | 任何人都不得出于任何原因调用此方法 |
| 2 | 此方法只能由授予权限的 s 调用AuthenticationROLE_ADMIN |
| 3 | 此方法只能由授予 和 权限的 s 调用AuthenticationdbROLE_ADMIN |
| 4 | 此方法只能由声明等于“my-audience”的 s 调用Princpalaud |
| 5 | 仅当 bean 的方法返回authzchecktrue |
|
您可以使用像上面一样的 bean 来添加编程授权。 |
使用方法参数
此外,Spring Security 提供了一种发现方法参数的机制,因此也可以在 SPEL 表达式中访问它们。
有关完整参考,Spring Security 用于发现参数名称。
默认情况下,对方法尝试以下选项。DefaultSecurityParameterNameDiscoverer
-
如果 Spring Security 的 Comments 存在于方法的单个参数上,则使用该值。 以下示例使用注释:
@P@P-
Java
-
Kotlin
import org.springframework.security.access.method.P; ... @PreAuthorize("hasPermission(#c, 'write')") public void updateContact(@P("c") Contact contact);import org.springframework.security.access.method.P ... @PreAuthorize("hasPermission(#c, 'write')") fun doSomething(@P("c") contact: Contact?)此表达式的目的是要求 current 具有专门针对此实例的权限。
AuthenticationwriteContact在幕后,这是通过使用 实现的,您可以自定义 value 以支持任何指定注释的 value 属性。
AnnotationParameterNameDiscoverer -
-
如果 Spring Data 的 Comments 存在于该方法的至少一个参数上,则使用该值。 以下示例使用注释:
@Param@Param-
Java
-
Kotlin
import org.springframework.data.repository.query.Param; ... @PreAuthorize("#n == authentication.name") Contact findContactByName(@Param("n") String name);import org.springframework.data.repository.query.Param ... @PreAuthorize("#n == authentication.name") fun findContactByName(@Param("n") name: String?): Contact?此表达式的目的是要求 that 等于 ,以便对调用进行授权。
nameAuthentication#getName在幕后,这是通过使用 实现的,您可以自定义 value 以支持任何指定注释的 value 属性。
AnnotationParameterNameDiscoverer -
-
如果使用参数编译代码,则使用标准 JDK 反射 API 来发现参数名称。 这适用于类和接口。
-parameters -
最后,如果使用调试符号编译代码,则使用调试符号会发现参数名称。 这不适用于接口,因为它们没有有关参数名称的调试信息。 对于接口,必须使用 annotations 或 the method。
-parameters
授权任意对象
Spring Security 还支持包装任何带有 Comments 其方法安全注释的对象。
实现此目的的最简单方法是标记任何返回您希望使用 Comments 授权的对象的方法。@AuthorizeReturnObject
例如,请考虑以下类:User
-
Java
-
Kotlin
public class User {
private String name;
private String email;
public User(String name, String email) {
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('user:read')")
public String getEmail() {
return this.email;
}
}class User (val name:String, @get:PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('user:read')") val email:String)给定一个像这样的接口:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
public class UserRepository {
@AuthorizeReturnObject
Optional<User> findByName(String name) {
// ...
}
}class UserRepository {
@AuthorizeReturnObject
fun findByName(name:String?): Optional<User?>? {
// ...
}
}然后,返回的任何内容都将像其他受 Spring Security 保护的组件一样受到保护:UserfindById
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Autowired
UserRepository users;
@Test
void getEmailWhenProxiedThenAuthorizes() {
Optional<User> securedUser = users.findByName("name");
assertThatExceptionOfType(AccessDeniedException.class).isThrownBy(() -> securedUser.get().getEmail());
}import jdk.incubator.vector.VectorOperators.Test
import java.nio.file.AccessDeniedException
import java.util.*
@Autowired
var users:UserRepository? = null
@Test
fun getEmailWhenProxiedThenAuthorizes() {
val securedUser: Optional<User> = users.findByName("name")
assertThatExceptionOfType(AccessDeniedException::class.java).isThrownBy{securedUser.get().getEmail()}
}在类级别使用@AuthorizeReturnObject
@AuthorizeReturnObject可以放置在类级别。但请注意,这意味着 Spring Security 将尝试代理任何返回对象,包括和其他类型的对象。
这通常不是您想要做的。StringInteger
如果要在其方法返回值类型(如 , 或这些类型的集合)的类或接口上使用,则还应按如下方式发布相应的内容:@AuthorizeReturnObjectintStringDoubleAuthorizationAdvisorProxyFactory.TargetVisitor
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Bean
static Customizer<AuthorizationAdvisorProxyFactory> skipValueTypes() {
return (factory) -> factory.setTargetVisitor(TargetVisitor.defaultsSkipValueTypes());
}@Bean
open fun skipValueTypes() = Customizer<AuthorizationAdvisorProxyFactory> {
it.setTargetVisitor(TargetVisitor.defaultsSkipValueTypes())
}|
您可以设置自己的代理,以自定义任何类型的代理 |
以编程方式代理
您还可以以编程方式代理给定对象。
为此,您可以自动装配提供的实例,该实例基于您配置的方法安全拦截器。
如果您使用的是 ,则这意味着默认情况下它将具有 、 、 和 的拦截器 。AuthorizationProxyFactory@EnableMethodSecurity@PreAuthorize@PostAuthorize@PreFilter@PostFilter
您可以通过以下方式代理 user 的实例:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Autowired
AuthorizationProxyFactory proxyFactory;
@Test
void getEmailWhenProxiedThenAuthorizes() {
User user = new User("name", "email");
assertThat(user.getEmail()).isNotNull();
User securedUser = proxyFactory.proxy(user);
assertThatExceptionOfType(AccessDeniedException.class).isThrownBy(securedUser::getEmail);
}@Autowired
var proxyFactory:AuthorizationProxyFactory? = null
@Test
fun getEmailWhenProxiedThenAuthorizes() {
val user: User = User("name", "email")
assertThat(user.getEmail()).isNotNull()
val securedUser: User = proxyFactory.proxy(user)
assertThatExceptionOfType(AccessDeniedException::class.java).isThrownBy(securedUser::getEmail)
}手动施工
如果您需要与 Spring Security 默认值不同的实例,您也可以定义自己的实例。
例如,如果您定义如下实例:AuthorizationProxyFactory
-
Java
-
Kotlin
import org.springframework.security.authorization.method.AuthorizationAdvisorProxyFactory.TargetVisitor;
import static org.springframework.security.authorization.method.AuthorizationManagerBeforeMethodInterceptor.preAuthorize;
// ...
AuthorizationProxyFactory proxyFactory = AuthorizationAdvisorProxyFactory.withDefaults();
// and if needing to skip value types
proxyFactory.setTargetVisitor(TargetVisitor.defaultsSkipValueTypes());import org.springframework.security.authorization.method.AuthorizationAdvisorProxyFactory.TargetVisitor;
import org.springframework.security.authorization.method.AuthorizationManagerBeforeMethodInterceptor.preAuthorize
// ...
val proxyFactory: AuthorizationProxyFactory = AuthorizationProxyFactory(preAuthorize())
// and if needing to skip value types
proxyFactory.setTargetVisitor(TargetVisitor.defaultsSkipValueTypes())然后,您可以包装 的任何实例,如下所示:User
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Test
void getEmailWhenProxiedThenAuthorizes() {
AuthorizationProxyFactory proxyFactory = AuthorizationAdvisorProxyFactory.withDefaults();
User user = new User("name", "email");
assertThat(user.getEmail()).isNotNull();
User securedUser = proxyFactory.proxy(user);
assertThatExceptionOfType(AccessDeniedException.class).isThrownBy(securedUser::getEmail);
}@Test
fun getEmailWhenProxiedThenAuthorizes() {
val proxyFactory: AuthorizationProxyFactory = AuthorizationAdvisorProxyFactory.withDefaults()
val user: User = User("name", "email")
assertThat(user.getEmail()).isNotNull()
val securedUser: User = proxyFactory.proxy(user)
assertThatExceptionOfType(AccessDeniedException::class.java).isThrownBy(securedUser::getEmail)
}代理集合
AuthorizationProxyFactory通过代理元素类型支持 Java 集合、流、数组、可选值和迭代器,并通过代理值类型来支持映射。
这意味着,在代理 of 对象时,以下操作也有效:List
-
Java
@Test
void getEmailWhenProxiedThenAuthorizes() {
AuthorizationProxyFactory proxyFactory = AuthorizationAdvisorProxyFactory.withDefaults();
List<User> users = List.of(ada, albert, marie);
List<User> securedUsers = proxyFactory.proxy(users);
securedUsers.forEach((securedUser) ->
assertThatExceptionOfType(AccessDeniedException.class).isThrownBy(securedUser::getEmail));
}代理类
在有限的情况下,代理 a 本身可能很有价值,并且也支持这一点。
这大致相当于调用 Spring Framework 对创建代理的支持。ClassAuthorizationProxyFactoryProxyFactory#getProxyClass
这很方便的一个地方是当你需要提前构造代理类时,就像使用 Spring AOT 一样。
支持所有方法安全注释
AuthorizationProxyFactory支持在应用程序中启用安全注释的任何方法。
它基于作为 bean 发布的任何类。AuthorizationAdvisor
由于默认情况下发布 、 、 和 advisors,因此您通常无需执行任何操作即可激活该功能。@EnableMethodSecurity@PreAuthorize@PostAuthorize@PreFilter@PostFilter
|
使用或位于代理后面的 SPEL 表达式,因此具有对对象的完全访问权限。 |
定制建议
如果您有安全建议也希望应用,您可以发布自己的安全建议,如下所示:AuthorizationAdvisor
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@EnableMethodSecurity
class SecurityConfig {
@Bean
static AuthorizationAdvisor myAuthorizationAdvisor() {
return new AuthorizationAdvisor();
}
}@EnableMethodSecurity
internal class SecurityConfig {
@Bean
fun myAuthorizationAdvisor(): AuthorizationAdvisor {
return AuthorizationAdvisor()
}
]Spring Security 会将该顾问添加到代理对象时添加的建议集中。AuthorizationProxyFactory
与 Jackson 合作
此功能的一个强大用途是从控制器返回一个受保护的值,如下所示:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Autowired
AuthorizationProxyFactory proxyFactory;
@GetMapping
User currentUser(@AuthenticationPrincipal User user) {
return this.proxyFactory.proxy(user);
}
}@RestController
class UserController {
@Autowired
var proxyFactory: AuthorizationProxyFactory? = null
@GetMapping
fun currentUser(@AuthenticationPrincipal user:User?): User {
return proxyFactory.proxy(user)
}
}-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Component
public class Null implements MethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler {
@Override
public Object handleDeniedInvocation(MethodInvocation methodInvocation, AuthorizationResult authorizationResult) {
return null;
}
}
// ...
@HandleAuthorizationDenied(handlerClass = Null.class)
public class User {
...
}@Component
class Null : MethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler {
override fun handleDeniedInvocation(methodInvocation: MethodInvocation?, authorizationResult: AuthorizationResult?): Any? {
return null
}
}
// ...
@HandleAuthorizationDenied(handlerClass = Null.class)
open class User {
...
}然后,您将看到基于用户授权级别的不同 JSON 序列化。
如果他们没有权限,则会看到:user:read
{
"name" : "name",
"email" : null
}如果他们确实拥有该权限,他们将看到:
{
"name" : "name",
"email" : "email"
}|
如果您还不想向未经授权的用户透露 JSON 密钥,您还可以添加 Spring Boot 属性以从序列化中排除 null 值。 |
使用 AOT
Spring Security 将扫描应用程序上下文中的所有 bean 以查找使用 .
找到一个代理类后,它将提前创建并注册适当的代理类。
它还将递归搜索其他也使用并相应地注册它们的嵌套对象。@AuthorizeReturnObject@AuthorizeReturnObject
例如,考虑以下 Spring Boot 应用程序:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@SpringBootApplication
public class MyApplication {
@RestController
public static class MyController { (1)
@GetMapping
@AuthorizeReturnObject
Message getMessage() { (2)
return new Message(someUser, "hello!");
}
}
public static class Message { (3)
User to;
String text;
// ...
@AuthorizeReturnObject
public User getTo() { (4)
return this.to;
}
// ...
}
public static class User { (5)
// ...
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MyApplication.class);
}
}@SpringBootApplication
open class MyApplication {
@RestController
open class MyController { (1)
@GetMapping
@AuthorizeReturnObject
fun getMessage():Message { (2)
return Message(someUser, "hello!")
}
}
open class Message { (3)
val to: User
val test: String
// ...
@AuthorizeReturnObject
fun getTo(): User { (4)
return this.to
}
// ...
}
open class User { (5)
// ...
}
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
SpringApplication.run(MyApplication.class)
}
}| 1 | - 首先,Spring Security 找到 beanMyController |
| 2 | - 找到一个使用 的方法,它代理返回值,并将该代理类注册到@AuthorizeReturnObjectMessageRuntimeHints |
| 3 | - 然后,它会遍历以查看它是否使用Message@AuthorizeReturnObject |
| 4 | - 找到一个使用 的方法,它代理返回值,并将该代理类注册到@AuthorizeReturnObjectUserRuntimeHints |
| 5 | - 最后,它遍历以查看它是否使用 ;什么也没找到,算法完成User@AuthorizeReturnObject |
很多时候 Spring Security 无法提前确定代理类,因为它可能隐藏在擦除的泛型类型中。
请考虑对以下内容的更改:MyController
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@RestController
public static class MyController {
@GetMapping
@AuthorizeReturnObject
List<Message> getMessages() {
return List.of(new Message(someUser, "hello!"));
}
}@RestController
static class MyController {
@AuthorizeReturnObject
@GetMapping
fun getMessages(): Array<Message> = arrayOf(Message(someUser, "hello!"))
}在这种情况下,泛型类型被擦除,因此 Spring Security 事先并不明显需要在运行时代理。Message
要解决此问题,您可以像这样发布:AuthorizeProxyFactoryHintsRegistrar
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
static SecurityHintsRegsitrar registerTheseToo(AuthorizationProxyFactory proxyFactory) {
return new AuthorizeReturnObjectHintsRegistrar(proxyFactory, Message.class);
}@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
fun registerTheseToo(proxyFactory: AuthorizationProxyFactory?): SecurityHintsRegistrar {
return AuthorizeReturnObjectHintsRegistrar(proxyFactory, Message::class.java)
}Spring Security 将注册该类,然后像以前一样遍历其类型。
在授权被拒绝时提供回退值
在某些情况下,你可能不希望在没有所需权限的情况下调用方法时引发 。
相反,您可能希望返回后处理结果,如掩码结果,或者在调用该方法之前发生授权被拒绝的情况下返回默认值。AuthorizationDeniedException
Spring Security 支持使用 @HandleAuthorizationDenied处理在方法调用时被拒绝的授权。
该处理程序适用于 @PreAuthorize 和 @PostAuthorize 注解中发生的被拒绝的授权,以及从方法调用本身引发的 AuthorizationDeniedException。
让我们考虑上一节中的示例,但不是创建将 an 转换为返回值,而是使用以下属性:AccessDeniedExceptionInterceptorAccessDeniedExceptionnullhandlerClass@HandleAuthorizationDenied
-
Java
-
Kotlin
public class NullMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler implements MethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler { (1)
@Override
public Object handleDeniedInvocation(MethodInvocation methodInvocation, AuthorizationResult authorizationResult) {
return null;
}
}
@Configuration
@EnableMethodSecurity
public class SecurityConfig {
@Bean (2)
public NullMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler nullMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler() {
return new NullMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler();
}
}
public class User {
// ...
@PreAuthorize(value = "hasAuthority('user:read')")
@HandleAuthorizationDenied(handlerClass = NullMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler.class)
public String getEmail() {
return this.email;
}
}class NullMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler : MethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler { (1)
override fun handleDeniedInvocation(methodInvocation: MethodInvocation, authorizationResult: AuthorizationResult): Any {
return null
}
}
@Configuration
@EnableMethodSecurity
class SecurityConfig {
@Bean (2)
fun nullMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler(): NullMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler {
return MaskMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler()
}
}
class User (val name:String, @PreAuthorize(value = "hasAuthority('user:read')") @HandleAuthorizationDenied(handlerClass = NullMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler::class) val email:String) (3)| 1 | 创建一个返回值的 实现MethodAuthorizationDeniedHandlernull |
| 2 | 将 注册为 beanNullMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler |
| 3 | 使用属性注释方法并传递 to@HandleAuthorizationDeniedNullMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandlerhandlerClass |
然后,您可以验证是否返回了一个值,而不是 :nullAccessDeniedException
|
你也可以用 而不是 create a 方法来注释你的类 |
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Autowired
UserRepository users;
@Test
void getEmailWhenProxiedThenNullEmail() {
Optional<User> securedUser = users.findByName("name");
assertThat(securedUser.get().getEmail()).isNull();
}@Autowired
var users:UserRepository? = null
@Test
fun getEmailWhenProxiedThenNullEmail() {
val securedUser: Optional<User> = users.findByName("name")
assertThat(securedUser.get().getEmail()).isNull()
}使用方法调用的 Denied 结果
在某些情况下,您可能希望返回从被拒绝的结果派生的安全结果。 例如,如果用户无权查看电子邮件地址,您可能希望对原始电子邮件地址应用一些掩码,即 [email protected] 将变为 use******@example.com。
对于这些方案,您可以覆盖 from the ,它将 MethodInvocationResult 作为参数。
让我们继续前面的示例,但不是返回 ,而是返回电子邮件的掩码值:handleDeniedInvocationResultMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandlernull
-
Java
-
Kotlin
public class EmailMaskingMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler implements MethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler { (1)
@Override
public Object handleDeniedInvocation(MethodInvocation methodInvocation, AuthorizationResult authorizationResult) {
return "***";
}
@Override
public Object handleDeniedInvocationResult(MethodInvocationResult methodInvocationResult, AuthorizationResult authorizationResult) {
String email = (String) methodInvocationResult.getResult();
return email.replaceAll("(^[^@]{3}|(?!^)\\G)[^@]", "$1*");
}
}
@Configuration
@EnableMethodSecurity
public class SecurityConfig {
@Bean (2)
public EmailMaskingMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler emailMaskingMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler() {
return new EmailMaskingMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler();
}
}
public class User {
// ...
@PostAuthorize(value = "hasAuthority('user:read')")
@HandleAuthorizationDenied(handlerClass = EmailMaskingMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler.class)
public String getEmail() {
return this.email;
}
}class EmailMaskingMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler : MethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler {
override fun handleDeniedInvocation(methodInvocation: MethodInvocation, authorizationResult: AuthorizationResult): Any {
return "***"
}
override fun handleDeniedInvocationResult(methodInvocationResult: MethodInvocationResult, authorizationResult: AuthorizationResult): Any {
val email = methodInvocationResult.result as String
return email.replace("(^[^@]{3}|(?!^)\\G)[^@]".toRegex(), "$1*")
}
}
@Configuration
@EnableMethodSecurity
class SecurityConfig {
@Bean
fun emailMaskingMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler(): EmailMaskingMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler {
return EmailMaskingMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler()
}
}
class User (val name:String, @PostAuthorize(value = "hasAuthority('user:read')") @HandleAuthorizationDenied(handlerClass = EmailMaskingMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler::class) val email:String) (3)| 1 | 创建一个 的实现,该实现返回 unauthorized result 值的掩码值MethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler |
| 2 | 将 注册为 beanEmailMaskingMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler |
| 3 | 使用属性注释方法并传递 to@HandleAuthorizationDeniedEmailMaskingMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandlerhandlerClass |
然后,您可以验证返回的是屏蔽电子邮件,而不是:AccessDeniedException
|
由于您有权访问原始 denied 值,因此请确保正确处理它,并且不要将其返回给调用方。 |
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Autowired
UserRepository users;
@Test
void getEmailWhenProxiedThenMaskedEmail() {
Optional<User> securedUser = users.findByName("name");
// email is [email protected]
assertThat(securedUser.get().getEmail()).isEqualTo("use******@example.com");
}@Autowired
var users:UserRepository? = null
@Test
fun getEmailWhenProxiedThenMaskedEmail() {
val securedUser: Optional<User> = users.findByName("name")
// email is [email protected]
assertThat(securedUser.get().getEmail()).isEqualTo("use******@example.com")
}在实现 时,你有几个选项可以返回什么类型:MethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler
-
一个值。
null -
一个非 null 值,遵循方法的返回类型。
-
引发异常,通常是 .这是默认行为。
AuthorizationDeniedException -
一种用于响应式应用程序的类型。
Mono
请注意,由于处理程序必须在应用程序上下文中注册为 bean,因此如果需要更复杂的逻辑,可以将依赖项注入其中。
除此之外,您还可以使用 或 或 ,以及 ,以获取与授权决策相关的更多详细信息。MethodInvocationMethodInvocationResultAuthorizationResult
根据可用参数决定返回的内容
考虑这样一个场景:不同的方法可能有多个掩码值,如果我们必须为每个方法创建一个处理程序,那么效率不会那么高,尽管这样做是完全可以的。
在这种情况下,我们可以使用通过 parameters 传递的信息来决定要做什么。
例如,我们可以创建一个自定义 annotation 和一个检测该 annotation 的处理程序,以决定返回什么掩码值:@Mask
-
Java
-
Kotlin
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationUtils;
@Target({ ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Mask {
String value();
}
public class MaskAnnotationDeniedHandler implements MethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler {
@Override
public Object handleDeniedInvocation(MethodInvocation methodInvocation, AuthorizationResult authorizationResult) {
Mask mask = AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(methodInvocation.getMethod(), Mask.class);
return mask.value();
}
}
@Configuration
@EnableMethodSecurity
public class SecurityConfig {
@Bean
public MaskAnnotationDeniedHandler maskAnnotationDeniedHandler() {
return new MaskAnnotationDeniedHandler();
}
}
@Component
public class MyService {
@PreAuthorize(value = "hasAuthority('user:read')")
@HandleAuthorizationDenied(handlerClass = MaskAnnotationDeniedHandler.class)
@Mask("***")
public String foo() {
return "foo";
}
@PreAuthorize(value = "hasAuthority('user:read')")
@HandleAuthorizationDenied(handlerClass = MaskAnnotationDeniedHandler.class)
@Mask("???")
public String bar() {
return "bar";
}
}import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationUtils
@Target(AnnotationTarget.FUNCTION, AnnotationTarget.CLASS)
@Retention(AnnotationRetention.RUNTIME)
annotation class Mask(val value: String)
class MaskAnnotationDeniedHandler : MethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler {
override fun handleDeniedInvocation(methodInvocation: MethodInvocation, authorizationResult: AuthorizationResult): Any {
val mask = AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(methodInvocation.method, Mask::class.java)
return mask.value
}
}
@Configuration
@EnableMethodSecurity
class SecurityConfig {
@Bean
fun maskAnnotationDeniedHandler(): MaskAnnotationDeniedHandler {
return MaskAnnotationDeniedHandler()
}
}
@Component
class MyService {
@PreAuthorize(value = "hasAuthority('user:read')")
@HandleAuthorizationDenied(handlerClass = MaskAnnotationDeniedHandler::class)
@Mask("***")
fun foo(): String {
return "foo"
}
@PreAuthorize(value = "hasAuthority('user:read')")
@HandleAuthorizationDenied(handlerClass = MaskAnnotationDeniedHandler::class)
@Mask("???")
fun bar(): String {
return "bar"
}
}现在,当访问被拒绝时,返回值将根据 annotation 来决定:@Mask
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Autowired
MyService myService;
@Test
void fooWhenDeniedThenReturnStars() {
String value = this.myService.foo();
assertThat(value).isEqualTo("***");
}
@Test
void barWhenDeniedThenReturnQuestionMarks() {
String value = this.myService.foo();
assertThat(value).isEqualTo("???");
}@Autowired
var myService: MyService
@Test
fun fooWhenDeniedThenReturnStars() {
val value: String = myService.foo()
assertThat(value).isEqualTo("***")
}
@Test
fun barWhenDeniedThenReturnQuestionMarks() {
val value: String = myService.foo()
assertThat(value).isEqualTo("???")
}与 Meta Annotation 支持相结合
您还可以将 与其他 Comments 结合使用,以减少和简化方法中的 Comments。
让我们考虑上一节中的示例,并与 : 合并 :@HandleAuthorizationDenied@HandleAuthorizationDenied@Mask
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Target({ ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@HandleAuthorizationDenied(handlerClass = MaskAnnotationDeniedHandler.class)
public @interface Mask {
String value();
}
@Mask("***")
public String myMethod() {
// ...
}@Target(AnnotationTarget.FUNCTION, AnnotationTarget.CLASS)
@Retention(AnnotationRetention.RUNTIME)
@HandleAuthorizationDenied(handlerClass = MaskAnnotationDeniedHandler::class)
annotation class Mask(val value: String)
@Mask("***")
fun myMethod(): String {
// ...
}现在,当您的方法中需要 mask 行为时,您不必记住添加这两个 Comments。 请务必阅读 Meta Annotations Support 部分,了解有关用法的更多详细信息。
迁移自@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity
如果您使用的是 ,则应迁移到 。@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity@EnableMethodSecurity
将全局方法安全性替换为方法安全性
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity 和 <global-method-security> 已弃用,分别取而代之的是 @EnableMethodSecurity 和 <method-security>。
新的 annotation 和 XML 元素默认激活 Spring 的 pre-post 注释并在内部使用。AuthorizationManager
这意味着以下两个清单在功能上是等效的:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
-
Xml
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)<global-method-security pre-post-enabled="true"/>和:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
-
Xml
@EnableMethodSecurity@EnableMethodSecurity<method-security/>对于不使用 pre-post 注释的应用程序,请确保将其关闭以避免激活不需要的行为。
例如,像这样的列表:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
-
Xml
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true)@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true)<global-method-security secured-enabled="true"/>应更改为:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
-
Xml
@EnableMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true, prePostEnabled = false)@EnableMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true, prePostEnabled = false)<method-security secured-enabled="true" pre-post-enabled="false"/>使用 Custom 而不是子类化@BeanDefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandler
作为性能优化,引入了一种新方法,该方法采用 a 而不是 .MethodSecurityExpressionHandlerSupplier<Authentication>Authentication
这允许 Spring Security 延迟查找 ,并在您使用而不是 .Authentication@EnableMethodSecurity@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity
但是,假设您的代码扩展并覆盖以返回自定义实例。
这将不再有效,因为 setup up calls 的 arrangement 改为。DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandlercreateSecurityExpressionRoot(Authentication, MethodInvocation)SecurityExpressionRoot@EnableMethodSecuritycreateEvaluationContext(Supplier<Authentication>, MethodInvocation)
令人高兴的是,这种级别的定制通常是不必要的。 相反,您可以使用所需的授权方法创建自定义 Bean。
例如,假设您希望对 .
您可以创建如下所示的自定义:@PostAuthorize("hasAuthority('ADMIN')")@Bean
-
Java
-
Kotlin
class MyAuthorizer {
boolean isAdmin(MethodSecurityExpressionOperations root) {
boolean decision = root.hasAuthority("ADMIN");
// custom work ...
return decision;
}
}class MyAuthorizer {
fun isAdmin(val root: MethodSecurityExpressionOperations): boolean {
val decision = root.hasAuthority("ADMIN");
// custom work ...
return decision;
}
}然后在 Comments 中引用它,如下所示:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@PreAuthorize("@authz.isAdmin(#root)")@PreAuthorize("@authz.isAdmin(#root)")我还是更喜欢子类DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandler
如果必须继续子类化 ,您仍然可以这样做。
相反,请覆盖该方法,如下所示:DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandlercreateEvaluationContext(Supplier<Authentication>, MethodInvocation)
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Component
class MyExpressionHandler extends DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandler {
@Override
public EvaluationContext createEvaluationContext(Supplier<Authentication> authentication, MethodInvocation mi) {
StandardEvaluationContext context = (StandardEvaluationContext) super.createEvaluationContext(authentication, mi);
MethodSecurityExpressionOperations delegate = (MethodSecurityExpressionOperations) context.getRootObject().getValue();
MySecurityExpressionRoot root = new MySecurityExpressionRoot(delegate);
context.setRootObject(root);
return context;
}
}@Component
class MyExpressionHandler: DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandler {
override fun createEvaluationContext(val authentication: Supplier<Authentication>,
val mi: MethodInvocation): EvaluationContext {
val context = super.createEvaluationContext(authentication, mi) as StandardEvaluationContext
val delegate = context.getRootObject().getValue() as MethodSecurityExpressionOperations
val root = MySecurityExpressionRoot(delegate)
context.setRootObject(root)
return context
}
}延伸阅读
现在您已经保护了应用程序的请求,如果您尚未保护其请求,请保护它。 您还可以进一步阅读有关测试应用程序或将 Spring Security 与应用程序的其他方面(如数据层或跟踪和指标)集成的信息。