|
此版本仍在开发中,尚未被视为稳定版本。最新的稳定版本请使用 Spring Framework 6.1.13! |
|
此版本仍在开发中,尚未被视为稳定版本。最新的稳定版本请使用 Spring Framework 6.1.13! |
Spring AOP 使用 JDK 动态代理或 CGLIB 为给定的
target 对象。JDK 动态代理内置于 JDK 中,而 CGLIB 是一种常见的
开源类定义库(重新打包为 )。spring-core
如果要代理的目标对象实现了至少一个接口,则 JDK 动态 proxy 的 Proxy 的 Interface,并且 target 类型实现的所有接口都是代理的。 如果目标对象未实现任何接口,则会创建一个 CGLIB 代理,该代理 是 target 类型的运行时生成的子类。
如果要强制使用 CGLIB 代理(例如,代理每个方法 为目标对象定义,而不仅仅是由其接口实现的对象), 您可以这样做。但是,您应该考虑以下问题:
-
final类不能被代理,因为它们不能被扩展。 -
final方法,因为它们不能被覆盖。 -
private方法,因为它们不能被覆盖。 -
不可见的方法 – 例如,父类中的 package-private 方法 来自不同的包——无法通知,因为它们实际上是私有的。
-
代理对象的构造函数不会被调用两次,因为 CGLIB 代理 实例是通过 Objenesis 创建的。但是,如果您的 JVM 不允许 构造函数绕过,您可能会看到双重调用和相应的调试日志 条目。
-
您的 CGLIB 代理使用可能会遇到 Java Module System 的限制。作为典型的 的情况下,当 部署在模块路径上。这种情况需要 JVM 引导标志,该标志不可用于模块。
java.lang--add-opens=java.base/java.lang=ALL-UNNAMED
要强制使用 CGLIB 代理,请设置属性
的元素设置为 true,如下所示:proxy-target-class<aop:config>
<aop:config proxy-target-class="true">
<!-- other beans defined here... -->
</aop:config>要在使用 @AspectJ 自动代理支持时强制使用 CGLIB 代理,请将元素的属性设置为 ,
如下:proxy-target-class<aop:aspectj-autoproxy>true
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true"/>|
多个部分折叠为单个统一的自动代理创建器
在运行时,这将应用任何部分(通常来自不同的 XML Bean 定义文件)指定的最强代理设置。
这也适用于 和 元素。 需要明确的是,使用 on 、 或 elements 会强制使用 CGLIB
他们三个的代理。 |
|
多个部分折叠为单个统一的自动代理创建器
在运行时,这将应用任何部分(通常来自不同的 XML Bean 定义文件)指定的最强代理设置。
这也适用于 和 元素。 需要明确的是,使用 on 、 或 elements 会强制使用 CGLIB
他们三个的代理。 |
了解 AOP 代理
Spring AOP 是基于代理的。掌握 在你编写自己的方面或使用任何 Spring 框架提供的基于 Spring AOP 的方面。
首先考虑你有一个普通的、未代理的对象引用 如下面的代码片段所示:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
public class SimplePojo implements Pojo {
public void foo() {
// this next method invocation is a direct call on the 'this' reference
this.bar();
}
public void bar() {
// some logic...
}
}class SimplePojo : Pojo {
fun foo() {
// this next method invocation is a direct call on the 'this' reference
this.bar()
}
fun bar() {
// some logic...
}
}如果在对象引用上调用方法,则会直接在 该对象引用,如下图所示:
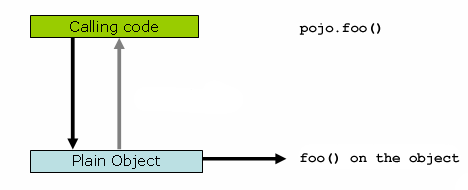
-
Java
-
Kotlin
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Pojo pojo = new SimplePojo();
// this is a direct method call on the 'pojo' reference
pojo.foo();
}
}fun main() {
val pojo = SimplePojo()
// this is a direct method call on the 'pojo' reference
pojo.foo()
}当客户端代码具有的引用是代理时,情况会略有变化。考虑一下 下图和代码片段如下:
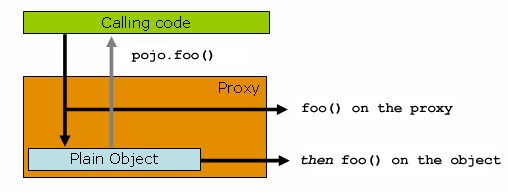
-
Java
-
Kotlin
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProxyFactory factory = new ProxyFactory(new SimplePojo());
factory.addInterface(Pojo.class);
factory.addAdvice(new RetryAdvice());
Pojo pojo = (Pojo) factory.getProxy();
// this is a method call on the proxy!
pojo.foo();
}
}fun main() {
val factory = ProxyFactory(SimplePojo())
factory.addInterface(Pojo::class.java)
factory.addAdvice(RetryAdvice())
val pojo = factory.proxy as Pojo
// this is a method call on the proxy!
pojo.foo()
}这里要了解的关键是,方法
的类具有对代理的引用。这意味着该方法调用
对象引用是对代理的调用。因此,代理可以将
与该特定方法调用相关的拦截器 (通知)。然而
一旦调用最终到达目标对象(
在这种情况下),它可能对自身进行的任何方法调用(例如 或 )都将针对引用调用,而不是针对代理调用。
这具有重要意义。这意味着 self invocation 不会产生
在与方法调用关联的建议中,获得运行的机会。换句话说,
self 调用将绕过该通知。main(..)MainSimplePojothis.bar()this.foo()thisthis
要解决此问题,您有以下选项。
- 避免自调用
-
最好的方法(这里松散地使用了“最佳”一词)是将代码重构为 self invocation 不会发生。这确实需要您做一些工作,但是 这是最好、侵入性最小的方法。
- 注入自引用
-
另一种方法是使用自我注射, 并通过 self reference 而不是 via 调用代理上的方法。
this - 用
AopContext.currentProxy() -
我们非常不鼓励使用最后一种方法,我们不愿指出它,以支持 前面的选项。但是,作为最后的手段,您可以选择将 logic 捆绑在 将类添加到 Spring AOP,如下例所示。
-
Java
-
Kotlin
public class SimplePojo implements Pojo {
public void foo() {
// This works, but it should be avoided if possible.
((Pojo) AopContext.currentProxy()).bar();
}
public void bar() {
// some logic...
}
}class SimplePojo : Pojo {
fun foo() {
// This works, but it should be avoided if possible.
(AopContext.currentProxy() as Pojo).bar()
}
fun bar() {
// some logic...
}
}使用 完全将你的代码耦合到 Spring AOP,它
使类本身知道它正在 AOP 上下文中使用的事实,这
减少了 AOP 的一些好处。它还要求 is
配置为公开代理,如下例所示:AopContext.currentProxy()ProxyFactory
-
Java
-
Kotlin
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProxyFactory factory = new ProxyFactory(new SimplePojo());
factory.addInterface(Pojo.class);
factory.addAdvice(new RetryAdvice());
factory.setExposeProxy(true);
Pojo pojo = (Pojo) factory.getProxy();
// this is a method call on the proxy!
pojo.foo();
}
}fun main() {
val factory = ProxyFactory(SimplePojo())
factory.addInterface(Pojo::class.java)
factory.addAdvice(RetryAdvice())
factory.isExposeProxy = true
val pojo = factory.proxy as Pojo
// this is a method call on the proxy!
pojo.foo()
}| AspectJ 编译时 weaving 和 load-time weaving 没有这种自调用 问题,因为它们在字节码中应用通知,而不是通过代理。 |
| AspectJ 编译时 weaving 和 load-time weaving 没有这种自调用 问题,因为它们在字节码中应用通知,而不是通过代理。 |