|
This version is still in development and is not considered stable yet. For the latest stable version, please use Spring Batch Documentation 5.1.2! |
|
This version is still in development and is not considered stable yet. For the latest stable version, please use Spring Batch Documentation 5.1.2! |
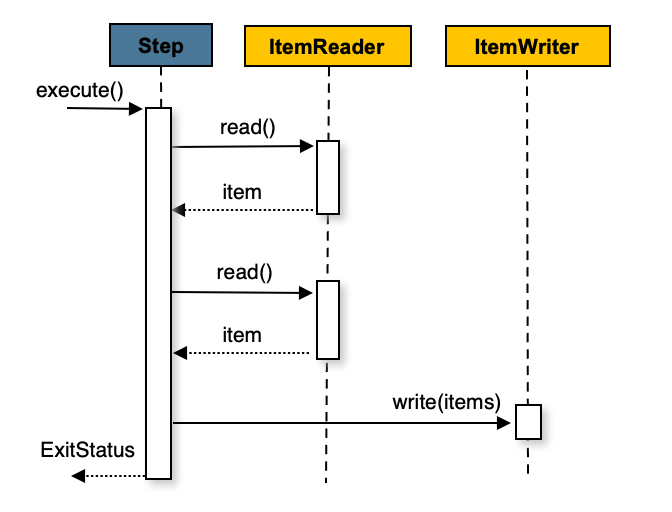
Spring Batch uses a “chunk-oriented” processing style in its most common
implementation. Chunk oriented processing refers to reading the data one at a time and
creating 'chunks' that are written out within a transaction boundary. Once the number of
items read equals the commit interval, the entire chunk is written out by the
ItemWriter, and then the transaction is committed. The following image shows the
process:
The following pseudo code shows the same concepts in a simplified form:
List items = new Arraylist();
for(int i = 0; i < commitInterval; i++){
Object item = itemReader.read();
if (item != null) {
items.add(item);
}
}
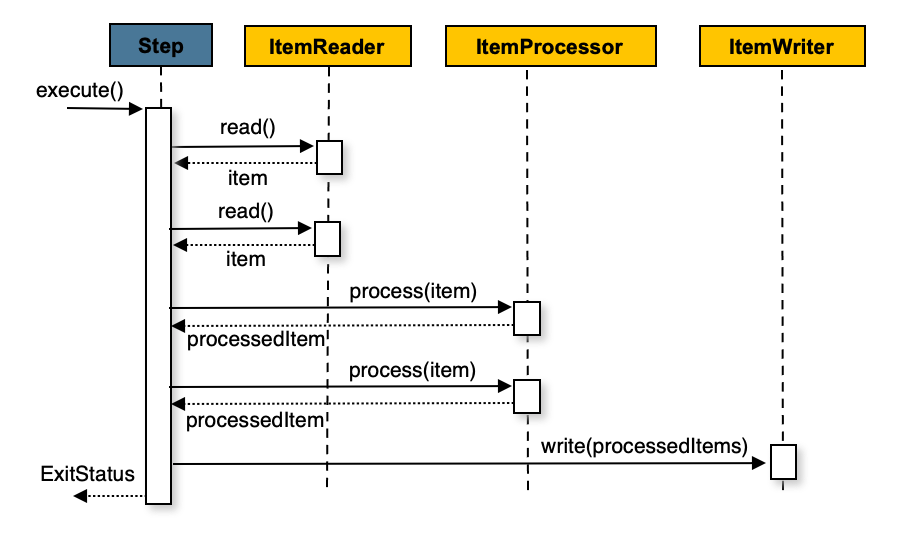
itemWriter.write(items);You can also configure a chunk-oriented step with an optional ItemProcessor
to process items before passing them to the ItemWriter. The following image
shows the process when an ItemProcessor is registered in the step:
The following pseudo code shows how this is implemented in a simplified form:
List items = new Arraylist();
for(int i = 0; i < commitInterval; i++){
Object item = itemReader.read();
if (item != null) {
items.add(item);
}
}
List processedItems = new Arraylist();
for(Object item: items){
Object processedItem = itemProcessor.process(item);
if (processedItem != null) {
processedItems.add(processedItem);
}
}
itemWriter.write(processedItems);For more details about item processors and their use cases, see the Item processing section.