|
对于最新的稳定版本,请使用 Spring Modulith 1.3.0! |
使用应用程序事件
为了使应用程序模块尽可能彼此分离,它们的主要交互方式应该是事件发布和使用。 这样可以避免原始模块了解所有可能感兴趣的参与方,这是启用应用程序模块集成测试的一个关键方面(请参阅集成测试应用程序模块)。
我们通常会发现应用程序组件是这样定义的:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class OrderManagement {
private final InventoryManagement inventory;
@Transactional
public void complete(Order order) {
// State transition on the order aggregate go here
// Invoke related functionality
inventory.updateStockFor(order);
}
}@Service
class OrderManagement(val inventory: InventoryManagement) {
@Transactional
fun complete(order: Order) {
inventory.updateStockFor(order)
}
}该方法在某种意义上创建了函数引力,因为它吸引了相关功能,从而与其他应用程序模块中定义的 Spring bean 进行交互。
这尤其使组件更难测试,因为我们需要有依赖于 bean 的实例可用,只是为了创建一个实例(参见 处理传出的依赖关系)。
这也意味着,每当我们想将更多功能与业务事件订单完成集成时,我们都必须接触该类。complete(…)OrderManagement
我们可以按如下方式更改应用程序模块交互:
ApplicationEventPublisher-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class OrderManagement {
private final ApplicationEventPublisher events;
private final OrderInternal dependency;
@Transactional
public void complete(Order order) {
// State transition on the order aggregate go here
events.publishEvent(new OrderCompleted(order.getId()));
}
}@Service
class OrderManagement(val events: ApplicationEventPublisher, val dependency: OrderInternal) {
@Transactional
fun complete(order: Order) {
events.publishEvent(OrderCompleted(order.id))
}
}请注意,一旦我们在主聚合上完成了状态转换,我们如何使用 Spring 的 Spring bean 来发布域事件,而不是依赖于其他应用程序模块的 Spring bean。
有关更加聚合驱动的事件发布方法,请参阅 Spring Data 的应用程序事件发布机制了解详细信息。
由于默认情况下事件发布是同步发生的,因此整体安排的事务语义与上面的示例相同。
这既是好的,因为我们得到了一个非常简单的一致性模型(要么订单的状态更改和库存更新都成功,要么都不成功),但也有坏处,因为更多触发的相关功能会扩大交易边界并可能导致整个交易失败,即使导致错误的功能并不重要。ApplicationEventPublisher
另一种解决方法是在事务提交时将事件使用转移到异步处理,并完全按照以下方式处理辅助功能:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Component
class InventoryManagement {
@Async
@TransactionalEventListener
void on(OrderCompleted event) { /* … */ }
}@Component
class InventoryManagement {
@Async
@TransactionalEventListener
fun on(event: OrderCompleted) { /* … */ }
}现在,这有效地将原始事务与侦听器的执行分离。 虽然这避免了原始业务事务的扩展,但它也带来了风险:如果侦听器由于任何原因失败,则事件发布将丢失,除非每个侦听器实际上都实现了自己的安全网。 更糟糕的是,这甚至不能完全起作用,因为系统甚至可能在调用方法之前就失败。
应用程序模块侦听器
要在事务本身中运行事务性事件侦听器,需要依次对其进行 Comments。@Transactional
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Component
class InventoryManagement {
@Async
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
@TransactionalEventListener
void on(OrderCompleted event) { /* … */ }
}@Component
class InventoryManagement {
@Async
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
@TransactionalEventListener
fun on(event: OrderCompleted) { /* … */ }
}为了简化应该描述通过事件集成模块的默认方式的声明, Spring Modulith 提供了快捷方式声明@ApplicationModuleListener
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Component
class InventoryManagement {
@ApplicationModuleListener
void on(OrderCompleted event) { /* … */ }
}@Component
class InventoryManagement {
@ApplicationModuleListener
fun on(event: OrderCompleted) { /* … */ }
}活动出版物注册表
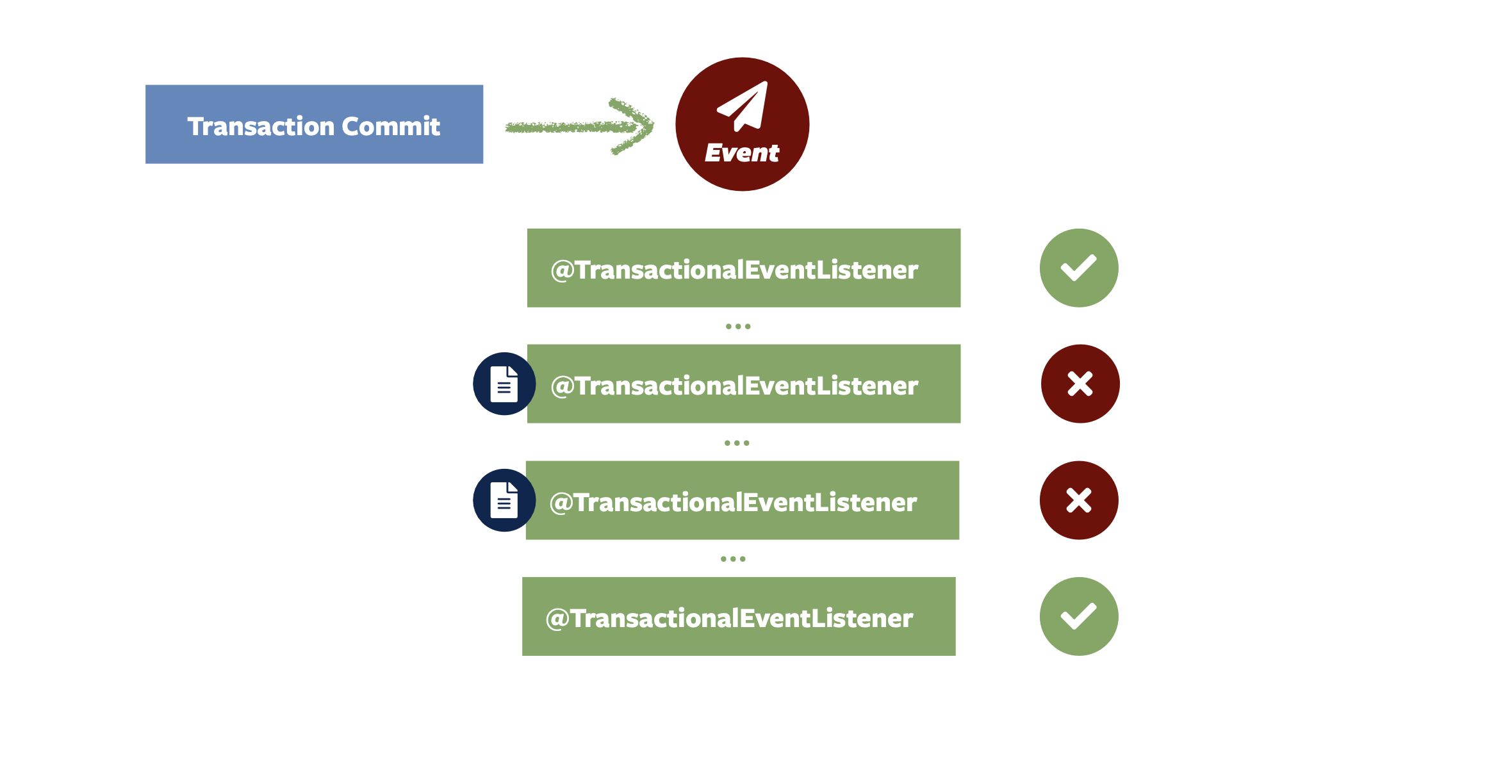
Spring Modulith 附带了一个事件发布注册表,该注册表挂接到 Spring 框架的核心事件发布机制中。 在事件发布时,它会找出将传递事件的事务性事件侦听器,并将每个事件侦听器的条目(深蓝色)写入事件发布日志,作为原始业务事务的一部分。
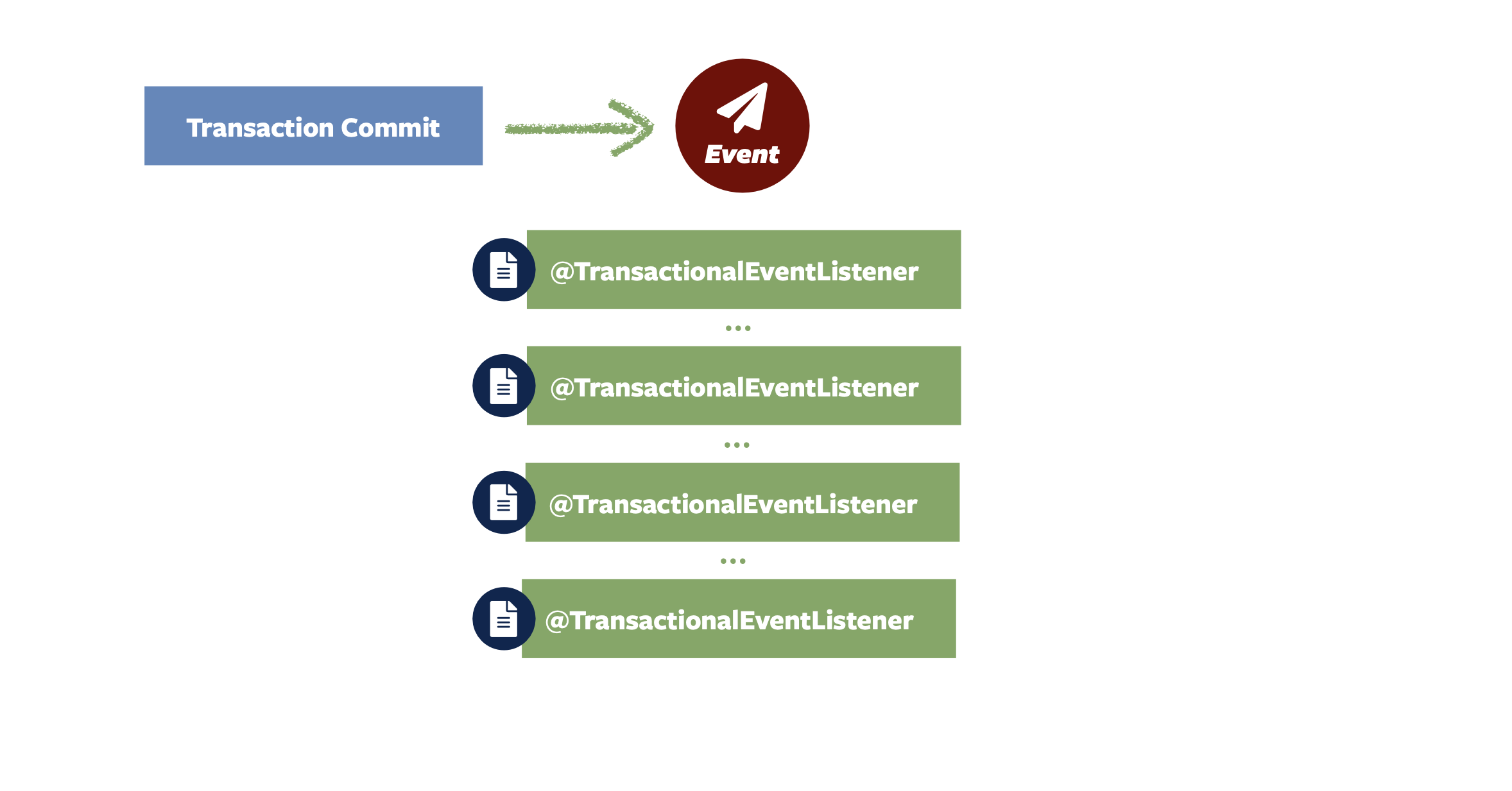
每个事务性事件侦听器都包装到一个方面中,如果侦听器执行成功,则该 Clock Entry(日志条目)标记为已完成。
如果侦听器失败,日志条目将保持不变,以便可以根据应用程序的需要部署重试机制。
可以通过spring.modulith.republish-outstanding-events-on-restart属性启用事件的自动重新发布。
管理事件发布
在应用程序的运行时,可能需要以多种方式管理事件发布。
在给定的时间后,可能必须将不完整的发布重新提交给相应的侦听器。
另一方面,完成的出版物可能必须从数据库中清除或移动到存档存储中。
由于对这种内务处理的需求因应用程序而异,Spring Modulith 提供了 API 来处理这两种类型的出版物。
该 API 可通过构件获得,您可以将其添加到应用程序中:spring-modulith-events-api
-
Maven
-
Gradle
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.modulith</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-modulith-events-api</artifactId>
<version>1.1.11</version>
</dependency>dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.modulith:spring-modulith-events-api:1.1.11'
}此工件包含两个主要抽象,它们可作为 Spring Bean 提供给应用程序代码:
-
CompletedEventPublications— 此界面允许访问所有已完成的事件发布,并提供 API 以立即从数据库或早于给定持续时间(例如,1 分钟)的已完成发布中清除所有这些事件。 -
IncompleteEventPublications-- 此界面允许访问所有未完成的事件发布,以重新提交与给定谓词匹配的发布,或者重新提交早于给定相对于原始发布日期的发布。Duration
活动发布存储库
为了实际编写事件发布日志,Spring Modulith 公开了一个 SPI 和支持事务的流行持久化技术的实现,比如 JPA、JDBC 和 MongoDB。
您可以通过将相应的 JAR 添加到您的 Spring Modulith 应用程序来选择要使用的持久性技术。
我们准备了专用的Starters来简化这项任务。EventPublicationRepository
当相应的配置属性 () 设置为 时,基于 JDBC 的实现可以为事件发布日志创建专用表。
有关详细信息,请参阅附录中的 Schema 概述。spring.modulith.events.jdbc.schema-initialization.enabledtrue
外部化事件
外部系统可能会对应用程序模块之间交换的某些事件感兴趣。 Spring Modulith 允许将选定的事件发布到各种消息代理。 要使用该支持,您需要执行以下步骤:
-
将特定于代理的 Spring Modulith 工件添加到您的项目中。
-
通过使用 Spring Modulith 或 jMolecules 的 Comments 来选择要外部化的事件类型。
@Externalized -
在 annotation 的值中指定特定于代理的路由目标。
要了解如何使用其他方式选择要外部化的事件,或在 broker 中自定义其路由,请查看 事件外部化基础。
支持的基础设施
| 代理 | 人工制品 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
卡 夫 卡 |
|
使用 Spring Kafka 与 broker 进行交互。 逻辑路由键将用作 |
AMQP |
|
使用 Spring AMQP 与任何兼容的代理进行交互。 例如,需要 Spring Rabbit 的显式依赖项声明。 逻辑路由密钥将用作 AMQP 路由密钥。 |
JMS 公司 |
|
使用 Spring 的核心 JMS 支持。 不支持路由键。 |
SQS |
|
使用 Spring Cloud AWS SQS 支持。 逻辑路由密钥将用作 SQS 消息组 ID。 设置路由密钥后,需要将 SQS 队列配置为 FIFO 队列。 |
社交网络 |
|
使用 Spring Cloud AWS SNS 支持。 逻辑路由密钥将用作 SNS 消息组 ID。 设置路由密钥后,需要将 SNS 配置为 FIFO 主题,并启用基于内容的重复数据删除。 |
事件外部化的基础
事件外部化对发布的每个应用程序事件执行三个步骤。
-
确定事件是否应该外部化 — 我们将其称为 “事件选择”。 默认情况下,仅选择位于 Spring Boot 自动配置包中并使用受支持的 Comments 之一进行注释的事件类型进行外部化。
@Externalized -
映射事件(可选)— 默认情况下,事件使用应用程序中的 Jackson 序列化为 JSON,并按原样发布。 映射步骤允许开发人员自定义表示,甚至将原始事件完全替换为适合外部方的表示。 请注意,映射步骤在待发布对象的实际序列化之前。
ObjectMapper -
确定路由目标 — 消息代理客户端需要一个逻辑目标来将消息发布到该目标。 目标通常标识物理基础设施(主题、交易所或队列,具体取决于代理),并且通常是从事件类型静态派生的。 除非在 Comments 中特别定义,否则 Spring Modulith 使用应用程序本地类型名称作为目标。 换句话说,在基包为 的 Spring Boot 应用程序中,事件类型将发布到 。
@Externalizedcom.acme.appcom.acme.app.sample.SampleEventsample.SampleEvent一些 broker 还允许定义一个相当动态的 routing key,该 key 用于实际目标中的不同目的。 默认情况下,不使用路由密钥。
基于 Comments 的事件外部化配置
要通过 annotation 定义自定义路由键,可以将 的模式 用于每个特定 annotation 中可用的 target/value 属性。
键可以是 SpEL 表达式,它将获取配置为根对象的事件实例。@Externalized$target::$key
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Externalized("customer-created::#{#this.getLastname()}") (2)
class CustomerCreated {
String getLastname() { (1)
// …
}
}@Externalized("customer-created::#{#this.getLastname()}") (2)
class CustomerCreated {
fun getLastname(): String { (1)
// …
}
}该事件通过访问器方法公开 customer 的姓氏。
然后,该方法通过 target 声明的分隔符后面的 expression in key expression 使用。CustomerCreated#this.getLastname()::
如果键计算变得更加复杂,建议将其委托给将事件作为参数的 Spring bean:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Externalized("…::#{@beanName.someMethod(#this)}")@Externalized("…::#{@beanName.someMethod(#this)}")编程事件外部化配置
该构件包含允许开发人员自定义上述所有步骤。spring-modulith-events-apiEventExternalizationConfiguration
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Configuration
class ExternalizationConfiguration {
@Bean
EventExternalizationConfiguration eventExternalizationConfiguration() {
return EventExternalizationConfiguration.externalizing() (1)
.select(EventExternalizationConfiguration.annotatedAsExternalized()) (2)
.mapping(SomeEvent.class, event -> …) (3)
.routeKey(WithKeyProperty.class, WithKeyProperty::getKey) (4)
.build();
}
}@Configuration
class ExternalizationConfiguration {
@Bean
fun eventExternalizationConfiguration(): EventExternalizationConfiguration {
EventExternalizationConfiguration.externalizing() (1)
.select(EventExternalizationConfiguration.annotatedAsExternalized()) (2)
.mapping(SomeEvent::class.java) { event -> … } (3)
.routeKey(WithKeyProperty::class.java, WithKeyProperty::getKey) (4)
.build()
}
}| 1 | 我们首先创建一个默认实例。EventExternalizationConfiguration |
| 2 | 我们通过调用上一个调用返回的实例上的某个方法来自定义事件选择。
此步骤从根本上禁用了应用程序基础包过滤器,因为我们现在只查找注释。
存在按类型、包、包和注释轻松选择事件的便捷方法。
此外,还有一个在一个步骤中定义选择和路由的快捷方式。select(…)Selector |
| 3 | 我们为实例定义一个映射步骤。
请注意,路由仍将由原始事件实例决定,除非你额外调用 router。SomeEvent….routeMapped() |
| 4 | 最后,我们通过定义一个方法 handle 来提取事件实例的值,从而确定路由键。
或者,可以通过在上一次调用返回的实例上使用 general 方法为单个事件生成 full。RoutingKeyroute(…)Router |
测试已发布的事件
以下部分描述了一种仅专注于跟踪 Spring 应用程序事件的测试方法。
有关测试使用 @ApplicationModuleListener 的模块的更整体方法,请查看方案 API。 |
Spring Modulith 能够将实例注入到测试方法中,以验证在被测业务操作过程中是否发布了一组特定的事件。@ApplicationModuleTestPublishedEvents
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@ApplicationModuleTest
class OrderIntegrationTests {
@Test
void someTestMethod(PublishedEvents events) {
// …
var matchingMapped = events.ofType(OrderCompleted.class)
.matching(OrderCompleted::getOrderId, reference.getId());
assertThat(matchingMapped).hasSize(1);
}
}@ApplicationModuleTest
class OrderIntegrationTests {
@Test
fun someTestMethod(events: PublishedEvents events) {
// …
val matchingMapped = events.ofType(OrderCompleted::class.java)
.matching(OrderCompleted::getOrderId, reference.getId())
assertThat(matchingMapped).hasSize(1)
}
}请注意,如何公开 API 以选择符合特定条件的事件。
验证由 AssertJ 断言结束,该断言验证预期的元素数。
如果无论如何都要将 AssertJ 用于这些断言,则还可以用作测试方法参数类型,并使用通过它提供的 Fluent 断言 API。PublishedEventsAssertablePublishedEvents
AssertablePublishedEvents-
Java
-
Kotlin
@ApplicationModuleTest
class OrderIntegrationTests {
@Test
void someTestMethod(AssertablePublishedEvents events) {
// …
assertThat(events)
.contains(OrderCompleted.class)
.matching(OrderCompleted::getOrderId, reference.getId());
}
}@ApplicationModuleTest
class OrderIntegrationTests {
@Test
fun someTestMethod(events: AssertablePublishedEvents) {
// …
assertThat(events)
.contains(OrderCompleted::class.java)
.matching(OrderCompleted::getOrderId, reference.getId())
}
}请注意,表达式返回的类型如何允许直接定义对已发布事件的约束。assertThat(…)
Spring Boot 事件注册表Starters
使用事务性事件发布日志需要将构件组合添加到您的应用程序中。
为了简化该任务,Spring Modulith 提供了以要使用的持久性技术为中心的入门 POM,并默认为基于 Jackson 的实现。
以下Starters可用:EventSerializer
-
spring-modulith-starter-jpa— 使用 JPA 作为持久化技术。 -
spring-modulith-starter-jdbc— 使用 JDBC 作为持久化技术。 也适用于基于 JPA 的应用程序,但绕过 JPA 提供程序以实现实际事件持久性。 -
spring-modulith-starter-mongodb— 在 Spring Data MongoDB 后面使用 MongoDB。 此外,还支持 MongoDB 事务,并且需要服务器的副本集设置才能与之交互。 可以通过将属性设置为 来禁用事务自动配置。spring.modulith.events.mongobd.transaction-management.enabledfalse -
spring-modulith-starter-neo4j— 在 Spring Data Neo4j 后面使用 Neo4j。