4. 使用应用程序事件
为了使应用程序模块尽可能彼此分离,它们的主要交互方式应该是事件发布和使用。 这样可以避免原始模块了解所有可能感兴趣的参与方,这是启用应用程序模块集成测试的一个关键方面(请参阅集成测试应用程序模块)。
我们通常会发现应用程序组件是这样定义的:
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class OrderManagement {
private final InventoryManagement inventory;
@Transactional
public void complete(Order order) {
// State transition on the order aggregate go here
// Invoke related functionality
inventory.updateStockFor(order);
}
}
这complete(…)方法创建函数引力,因为它吸引了相关功能,从而与其他应用程序模块中定义的 Spring bean 进行交互。
这尤其使组件更难测试,因为我们需要有依赖于 bean 的实例可用,只是为了创建一个OrderManagement(参见 处理传出的依赖关系)。
这也意味着,每当我们想将更多功能与业务事件订单完成集成时,我们都必须接触该类。
我们可以按如下方式更改应用程序模块交互:
ApplicationEventPublisher@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class OrderManagement {
private final ApplicationEventPublisher events;
private final OrderInternal dependency;
@Transactional
public void complete(Order order) {
// State transition on the order aggregate go here
events.publishEvent(new OrderCompleted(order.getId()));
}
}
请注意,我们如何使用 Spring 的ApplicationEventPublisher发布域事件,在主聚合上完成状态转换后。
有关更加聚合驱动的事件发布方法,请参阅 Spring Data 的应用程序事件发布机制了解详细信息。
由于默认情况下事件发布是同步发生的,因此整体安排的事务语义与上面的示例相同。
这既是好的,因为我们得到了一个非常简单的一致性模型(要么订单的状态更改和库存更新都成功,要么都不成功),但也有坏处,因为更多触发的相关功能会扩大交易边界并可能导致整个交易失败,即使导致错误的功能并不重要。
另一种解决方法是在事务提交时将事件使用转移到异步处理,并完全按照以下方式处理辅助功能:
@Component
class InventoryManagement {
@Async
@TransactionalEventListener
void on(OrderCompleted event) { /* … */ }
}
现在,这有效地将原始事务与侦听器的执行分离。 虽然这避免了原始业务事务的扩展,但它也带来了风险:如果侦听器由于任何原因失败,则事件发布将丢失,除非每个侦听器实际上都实现了自己的安全网。 更糟糕的是,这甚至不能完全起作用,因为系统甚至可能在调用方法之前就失败。
4.1. 应用程序模块监听器
要在事务本身中运行事务性事件侦听器,需要用@Transactional挨次。
@Component
class InventoryManagement {
@Async
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
@TransactionalEventListener
void on(OrderCompleted event) { /* … */ }
}
为了简化应该描述通过事件集成模块的默认方式的声明, Spring Modulith 提供了@ApplicationModuleListener对声明进行快捷方式
@Component
class InventoryManagement {
@ApplicationModuleListener
void on(OrderCompleted event) { /* … */ }
}
4.2. Event Publication Registry
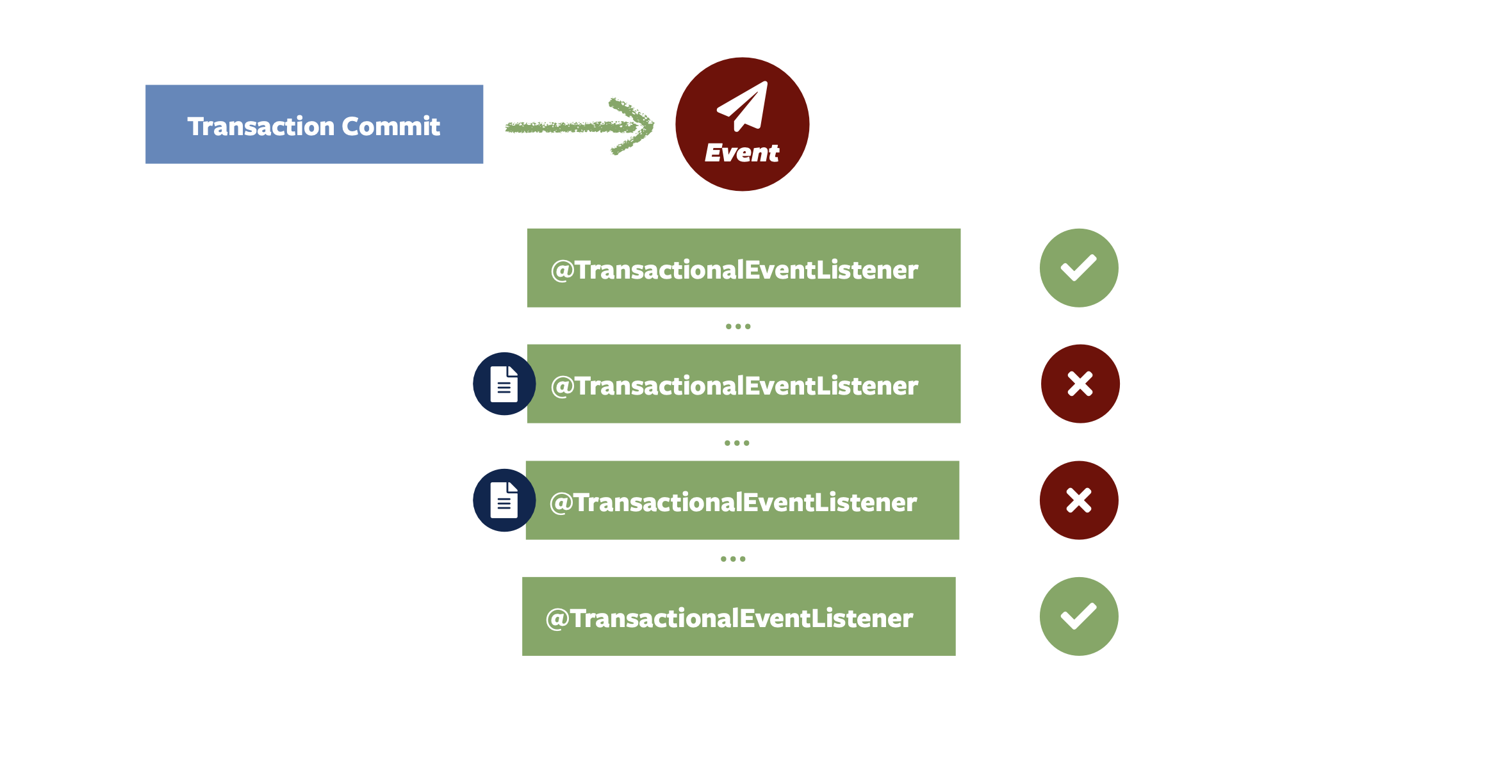
Spring Modulith 附带了一个事件发布注册表,该注册表挂接到 Spring 框架的核心事件发布机制中。 在事件发布时,它会找出将传递事件的事务性事件侦听器,并将每个事件侦听器的条目(深蓝色)写入事件发布日志,作为原始业务事务的一部分。
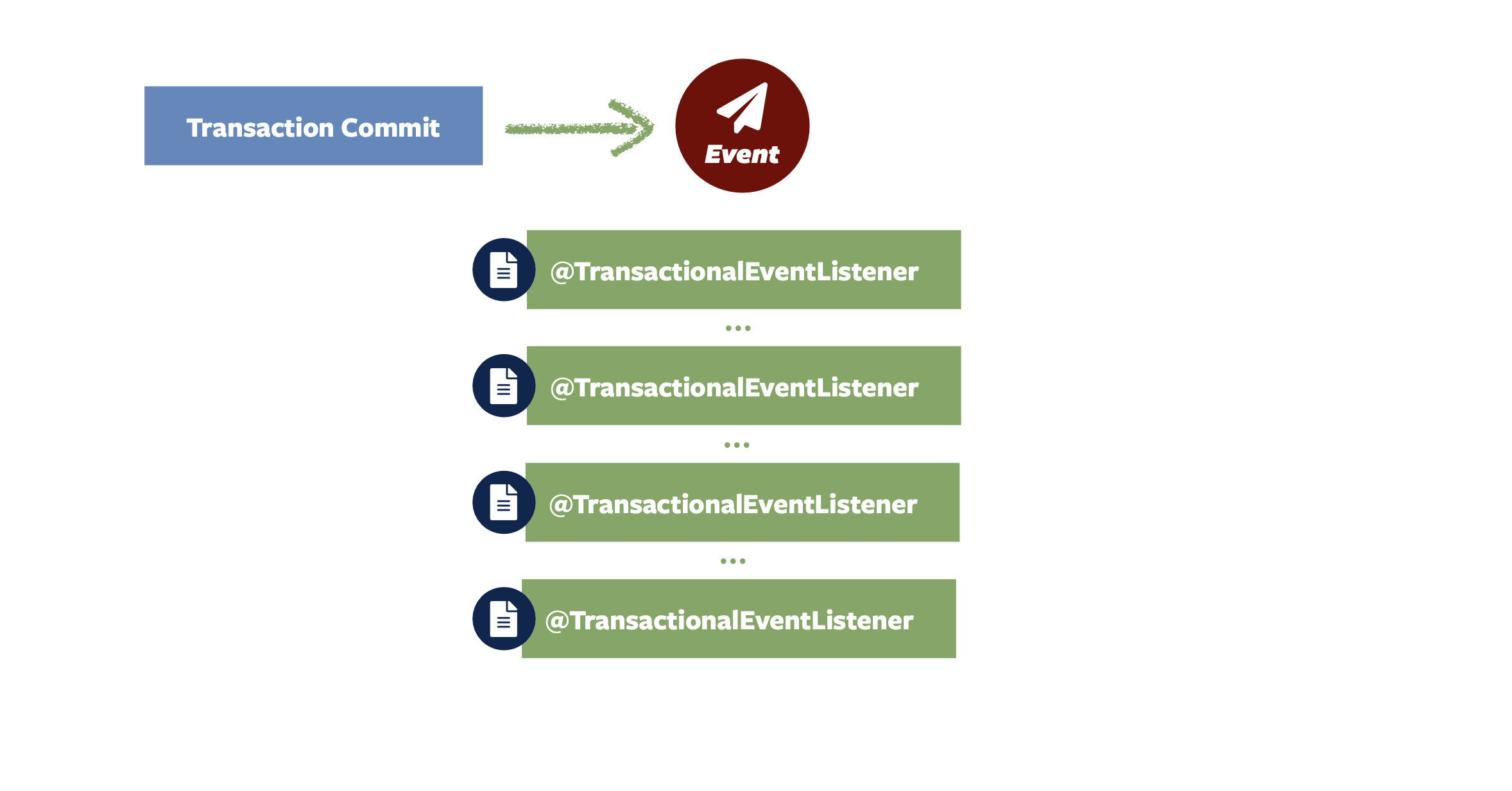
每个事务性事件侦听器都包装到一个方面中,如果侦听器执行成功,则该 Clock Entry(日志条目)标记为已完成。
如果侦听器失败,日志条目将保持不变,以便可以根据应用程序的需要部署重试机制。
可以通过设置spring.modulith.republish-outstanding-events-on-restartproperty 设置为true.
请注意,仅建议将此选项用于单实例应用程序部署。
为了更灵活的安排,EventPublicationRegistry公开一个方法….findIncompletePublications()可以从用户代码中调用。
4.3. 事件发布存储库
为了实际写入事件发布日志,Spring Modulith 公开了一个EventPublicationRepositorySPI 和支持事务的常用持久性技术(如 JPA、JDBC 和 MongoDB)的实现。
您可以通过将相应的 JAR 添加到您的 Spring Modulith 应用程序来选择要使用的持久性技术。
我们准备了专用的Starters来简化这项任务。
基于 JDBC 的实现可以在相应的配置属性 (spring.modulith.events.jdbc-schema-initialization.enabled) 设置为true.
有关详细信息,请参阅附录中的 Schema 概述。
4.4. 事件序列化器
每个日志条目都包含序列化形式的原始事件。
这EventSerializerabstraction 包含在spring-modulith-events-core允许插入不同的策略,以便将事件实例转换为适合数据存储的格式。
Spring Modulith 通过spring-modulith-events-jacksonartifact 中,它会注册一个JacksonEventSerializer使用ObjectMapper默认情况下,通过标准 Spring Boot 自动配置。
4.5. 自定义事件发布日期
默认情况下,Event Publication Registry 将使用Clock.systemUTC()作为事件发布日期。
如果要自定义此内容,请在应用程序上下文中注册 clock 类型的 bean:
@Configuration
class MyConfiguration {
@Bean
Clock myCustomClock() {
return … // Your custom Clock instance created here.
}
}
4.6. Spring Boot 事件注册表Starters
使用事务性事件发布日志需要将构件组合添加到您的应用程序中。
为了简化这项任务,Spring Modulith 提供了以要使用的持久化技术为中心的初始 POM,默认使用基于 Jackson 的EventSerializer实现。
以下Starters可用:
-
spring-modulith-starter-jpa— 使用 JPA 作为持久化技术。 -
spring-modulith-starter-jdbc— 使用 JDBC 作为持久化技术。 也适用于基于 JPA 的应用程序,但绕过 JPA 提供程序以实现实际事件持久性。 -
spring-modulith-starter-mongodb— 在 Spring Data MongoDB 后面使用 MongoDB。 此外,还支持 MongoDB 事务,并且需要服务器的副本集设置才能与之交互。 可以通过设置spring.modulith.events.mongobd.transaction-management.enabledproperty 设置为false.
4.7. 集成测试应用程序模块使用事件
与其他模块的 Spring bean 交互的应用程序模块的集成测试通常会模拟这些 bean,测试用例通过验证该 mock bean 是否以特定方式调用来验证交互。
@ApplicationModuleTest
class OrderIntegrationTests {
@MockBean SomeOtherComponent someOtherComponent;
@Test
void someTestMethod() {
// Given
// When
// Then
verify(someOtherComponent).someMethodCall();
}
}
在基于事件的应用程序交互模型中,对另一个应用程序模块的 Spring bean 的依赖性已经消失,我们没有什么需要验证的。
Spring Modulith 的@ApplicationModuleTest启用获取PublishedEvents实例注入到测试方法中,以验证在被测业务作过程中是否已发布一组特定的事件。
@ApplicationModuleTest
class OrderIntegrationTests {
@Test
void someTestMethod(PublishedEvents events) {
// …
var matchingMapped = events.ofType(OrderCompleted.class)
.matching(OrderCompleted::getOrderId, reference.getId());
assertThat(matchingMapped).hasSize(1);
}
}
请注意,如何作PublishedEvents公开 API 以选择符合特定条件的事件。
验证由 AssertJ 断言结束,该断言验证预期的元素数。
如果您仍然将 AssertJ 用于这些断言,则还可以使用AssertablePublishedEvents作为测试方法参数类型,并使用通过该 API 提供的 Fluent 断言 API。
AssertablePublishedEvents验证事件发布@ApplicationModuleTest
class OrderIntegrationTests {
@Test
void someTestMethod(AssertablePublishedEvents events) {
// …
assertThat(events)
.contains(OrderCompleted.class)
.matching(OrderCompleted::getOrderId, reference.getId());
}
}
请注意,由assertThat(…)expression 允许直接定义对已发布事件的约束。